[2025/06/10 ~ 15] 이번 주에 살펴볼 만한 AI/ML 논문 모음
PyTorchKR



-
이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 첫째로 비디오 생성 분야에서의 기술적 진보와 함께 장기적인 시공간 일관성을 유지하는 모델에 대한 관심이 높아진 것을 알 수 있습니다. Seedance 1.0과 같은 고성능 비디오 생성 모델은 텍스트 및 이미지 입력을 통합하여 고해상도, 고품질의 영상을 빠르게 생성하는 데 초점을 맞추고 있으며, 장기 기억 메커니즘을 도입한 비디오 월드 모델은 이전에 생성된 환경을 잊지 않고 일관성 있게 재현하는 문제를 해결하려는 시도를 보여줍니다. 이는 영상 생성의 현실감과 내러티브 연속성을 동시에 추구하는 최근 연구의 흐름을 반영합니다.
-
둘째로, 멀티모달 대형 언어 모델(MLLM, Multimodal-LLM)과 시각-언어 모델(VLM, Vision-Language Model)의 효율적인 활용과 시각적 추론 능력 향상에 관한 연구가 활발합니다. ReVisiT와 같은 방법은 시각 토큰을 텍스트 생성 과정에 효과적으로 통합하여 시각적 근거 없는 응답 문제를 완화하며, ReasonMap 벤치마크는 세밀한 시각적 이해와 공간 추론 능력을 평가하여 MLLM의 한계를 진단합니다. 또한, LOCATE 3D는 3D 장면에서 객체 위치를 정확히 파악하는 자가 지도 학습 기반 접근법을 제시하여 실제 로봇 및 증강현실 적용 가능성을 넓히고 있습니다. 이러한 연구들은 시각 정보와 언어 정보를 통합하여 복잡한 인지 및 추론 문제를 해결하려는 멀티모달 AI의 발전 방향을 보여줍니다.
-
마지막으로, 자가 개선이 가능한 AI 에이전트와 이들 간의 통신 및 보안 문제에 대한 연구가 주목받고 있습니다. Darwin Godel Machine은 AI가 스스로 코드를 수정하고 성능을 향상시키는 자율적 자기개선 시스템을 제안하며, AI 발전의 자동화 가능성을 탐구합니다. 또한, AI 에이전트 간 상호작용을 위한 표준화된 프로토콜 부재 문제를 분석하고 미래 방향을 제시하는 연구와, 다양한 공격 시나리오에 대응하는 AI 에이전트 보안 평가 프레임워크인 DoomArena는 AI 시스템의 신뢰성과 안전성 확보에 중요한 기여를 하고 있습니다. 이처럼 AI 에이전트의 협력, 자율성, 보안 측면에서의 연구가 점차 중요해지고 있음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Seedance 1.0: 고성능 영상 생성 모델의 한계 탐구 / Seedance 1.0: Exploring the Boundaries of Video Generation Models
논문 소개
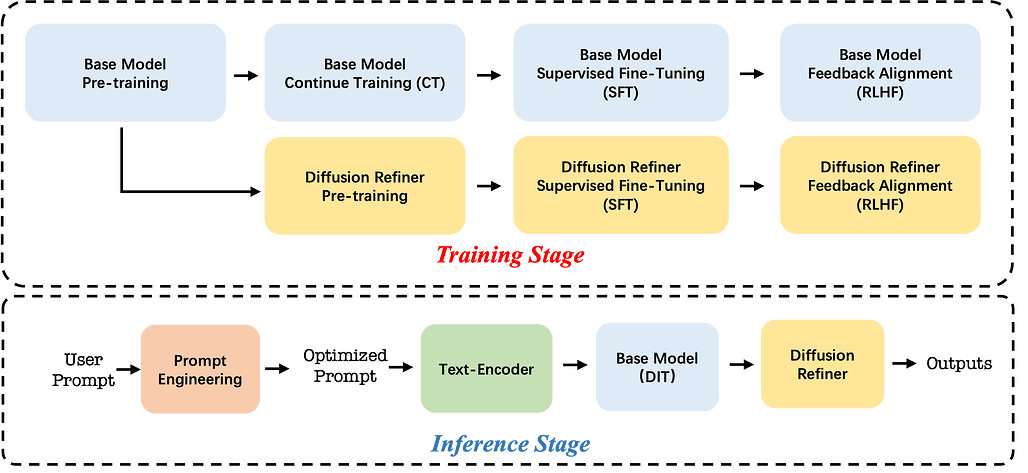
Seedance 1.0은 확산 모델(diffusion modeling)을 기반으로 한 고성능 비디오 생성 모델로, 프롬프트 준수, 동작 타당성, 시각적 품질 간의 균형 문제를 해결하고자 개발되었습니다. 다중 출처 데이터 큐레이션과 정밀한 비디오 캡셔닝을 통해 다양한 시나리오 학습을 가능하게 하며, 텍스트-투-비디오(text-to-video)와 이미지-투-비디오(image-to-video) 작업을 동시에 지원하는 효율적인 아키텍처와 훈련 패러다임을 제안합니다. 또한, 세밀한 감독 미세조정과 비디오 특화 강화학습(RLHF)을 활용하여 성능을 향상시키고, 다단계 증류 및 시스템 최적화를 통해 약 10배의 추론 속도 개선을 달성하였습니다. 결과적으로 Seedance 1.0은 1080p 해상도에서 5초 분량의 영상을 약 41.4초 만에 생성하며, 구조적 안정성과 시공간적 유동성, 복잡한 다중 주제 상황에서의 정확한 지시 준수, 일관된 내러티브 연속성을 모두 갖춘 우수한 비디오 생성 성능을 보입니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
확산 모델링(diffusion modeling) 분야에서 주목할 만한 혁신은 영상 생성의 급속한 발전을 이끌었으나, 현존하는 기초 모델은 여전히 프롬프트 준수, 움직임의 타당성, 시각적 품질을 동시에 균형 있게 달성하는 데 중요한 과제에 직면해 있습니다. 본 보고서에서는 Seedance 1.0을 소개합니다. Seedance 1.0은 고성능이면서 추론 효율성이 뛰어난 영상 기초 생성 모델로, 다음과 같은 핵심 기술적 개선 사항을 통합하였습니다: (i) 정밀하고 의미 있는 영상 캡셔닝으로 보강된 다중 출처 데이터 큐레이션을 통해 다양한 시나리오에 걸친 포괄적 학습 가능; (ii) 다중 샷 생성(native multi-shot generation)을 본질적으로 지원하고 텍스트-투-비디오(text-to-video) 및 이미지-투-비디오(image-to-video) 과제를 공동 학습할 수 있는 효율적인 아키텍처 설계 및 제안된 학습(paradigm) 방식; (iii) 세밀한 감독 학습(fine-grained supervised fine-tuning)과 다차원 보상 메커니즘을 활용한 영상 특화 RLHF(강화학습을 통한 인간 피드백, Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) 기반의 신중하게 최적화된 사후 학습(post-training) 기법을 통한 전반적 성능 향상; (iv) 다단계 증류(multi-stage distillation) 전략과 시스템 수준 최적화를 통해 약 10배의 추론 속도 향상을 달성한 우수한 모델 가속화. Seedance 1.0은 NVIDIA-L20 환경에서 1080p 해상도의 5초 영상을 단 41.4초 만에 생성할 수 있습니다. 최첨단 영상 생성 모델과 비교할 때, Seedance 1.0은 구조적 안정성과 우수한 시공간적 유동성(spatiotemporal fluidity)을 갖춘 고품질의 빠른 영상 생성, 복잡한 다중 주제 상황에서의 정밀한 지시 준수, 일관된 주제 표현을 유지하는 본질적 다중 샷 내러티브 일관성(native multi-shot narrative coherence) 측면에서 두드러진 성능을 보입니다.
Notable breakthroughs in diffusion modeling have propelled rapid improvements in video generation, yet current foundational model still face critical challenges in simultaneously balancing prompt following, motion plausibility, and visual quality. In this report, we introduce Seedance 1.0, a high-performance and inference-efficient video foundation generation model that integrates several core technical improvements: (i) multi-source data curation augmented with precision and meaningful video captioning, enabling comprehensive learning across diverse scenarios; (ii) an efficient architecture design with proposed training paradigm, which allows for natively supporting multi-shot generation and jointly learning of both text-to-video and image-to-video tasks. (iii) carefully-optimized post-training approaches leveraging fine-grained supervised fine-tuning, and video-specific RLHF with multi-dimensional reward mechanisms for comprehensive performance improvements; (iv) excellent model acceleration achieving ~10x inference speedup through multi-stage distillation strategies and system-level optimizations. Seedance 1.0 can generate a 5-second video at 1080p resolution only with 41.4 seconds (NVIDIA-L20). Compared to state-of-the-art video generation models, Seedance 1.0 stands out with high-quality and fast video generation having superior spatiotemporal fluidity with structural stability, precise instruction adherence in complex multi-subject contexts, native multi-shot narrative coherence with consistent subject representation.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
ReVisiT: LVLM의 효율적 유도 디코딩을 위한 비전 토큰 내 언어 사전 정보 공개 및 재고찰 / Revisit What You See: Disclose Language Prior in Vision Tokens for Efficient Guided Decoding of LVLMs
논문 소개
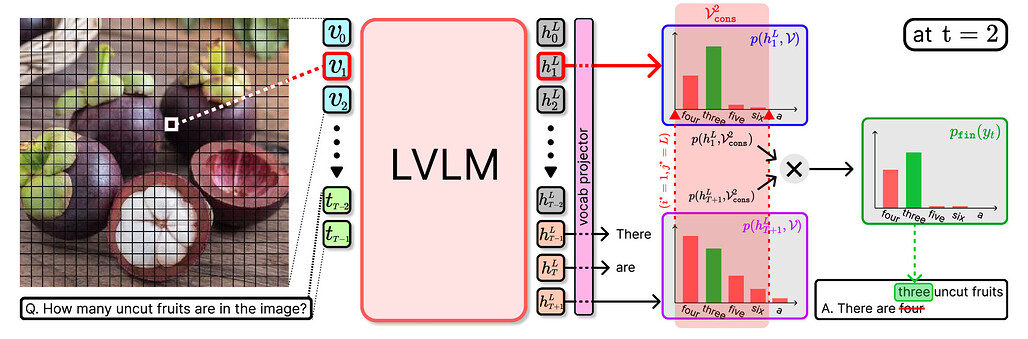
대규모 시각-언어 모델(LVLM)은 시각 인식과 언어 이해를 통합하여 다양한 멀티모달 작업에서 우수한 성능을 보이나, 기존 디코딩 방식은 시각 정보를 충분히 활용하지 못해 시각적 근거가 부족한 응답을 생성하는 문제가 있습니다. 제안된 ReVisiT 방법은 비전 토큰(vision tokens)의 의미 정보를 텍스트 토큰 분포 공간에 투영하고, 각 디코딩 단계에서 제한된 발산 최소화(constrained divergence minimization)를 통해 가장 관련성 높은 비전 토큰을 동적으로 선택하여 텍스트 생성 과정을 효과적으로 안내합니다. 이를 통해 시각적 의미를 보다 잘 반영한 출력을 생성하며, 추가 학습이나 복잡한 추론 절차 없이도 계산 비용을 크게 증가시키지 않고 시각적 근거 성능을 향상시킵니다. 세 가지 LVLM 환각(hallucination) 벤치마크와 두 가지 최신 LVLM에서 실험한 결과, ReVisiT는 최첨단 기법 대비 경쟁력 있는 성능을 보이면서 최대 2배까지 계산 비용을 절감하는 효과를 입증하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 비전-언어 모델(LVLM)은 시각 인지와 언어 이해를 통합하여 다양한 멀티모달 작업에서 뛰어난 성능을 보여주고 있습니다. 그러나 기존 LVLM의 디코딩 전략은 시각 정보를 효과적으로 활용하지 못해 시각적으로 근거 없는 응답을 생성하는 경우가 많습니다. 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위한 여러 접근법이 제안되었으나, 대부분 추가 학습, 다단계 추론 절차 또는 외부 모델 의존성을 필요로 합니다. 본 논문에서는 ReVisiT라는 간단하면서도 효과적인 디코딩 방법을 제안합니다. ReVisiT는 비전 토큰을 참조하여 LVLM의 텍스트 생성 과정을 안내합니다. 본 방법은 비전 토큰에 내재된 의미 정보를 텍스트 토큰 분포 공간으로 사영(projection)하고, 제한된 발산 최소화(constrained divergence minimization)를 통해 각 디코딩 단계에서 가장 관련성 높은 비전 토큰을 동적으로 선택합니다. 선택된 비전 토큰은 시각적 의미를 보다 잘 반영하도록 출력 분포를 정제하는 데 활용됩니다. 두 가지 최신 LVLM과 세 가지 LVLM 환각(hallucination) 벤치마크에서 수행한 실험 결과, ReVisiT는 최소한의 계산 비용으로 시각적 근거를 일관되게 향상시켰습니다. 또한, 본 방법은 최첨단 기준선 대비 경쟁력 있거나 우수한 성능을 달성하면서 계산 비용을 최대 2배까지 절감하였습니다.
Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across various multimodal tasks by integrating visual perception with language understanding. However, conventional decoding strategies of LVLMs often fail to successfully utilize visual information, leading to visually ungrounded responses. While various approaches have been proposed to address this limitation, they typically require additional training, multi-step inference procedures, or external model dependencies. This paper introduces ReVisiT, a simple yet effective decoding method that references vision tokens to guide the text generation process in LVLMs. Our approach leverages the semantic information embedded within vision tokens by projecting them into the text token distribution space, and dynamically selecting the most relevant vision token at each decoding step through constrained divergence minimization. This selected vision token is then used to refine the output distribution to better incorporate visual semantics. Experiments on three LVLM hallucination benchmarks with two recent LVLMs demonstrate that ReVisiT consistently enhances visual grounding with minimal computational overhead. Moreover, our method achieves competitive or superior results relative to state-of-the-art baselines while reducing computational costs for up to 2\times.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
장기 공간 기억을 활용한 비디오 월드 모델 / Video World Models with Long-term Spatial Memory
논문 소개
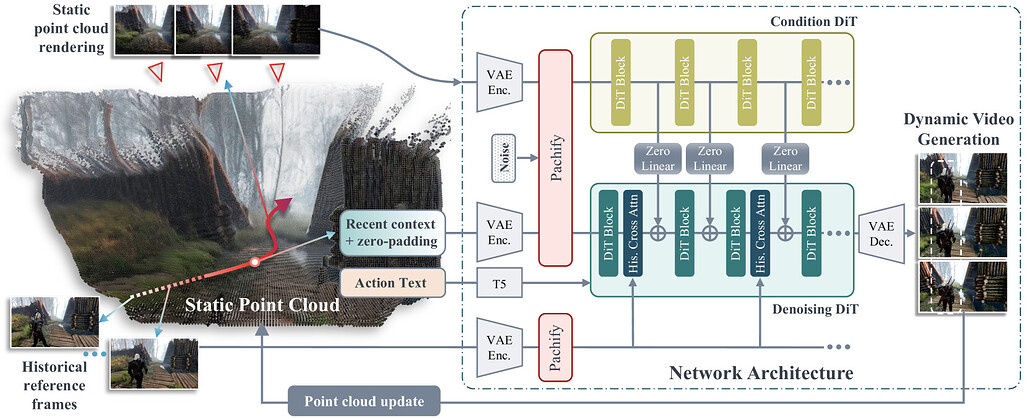
비디오 월드 모델은 카메라 움직임이나 텍스트 프롬프트 같은 제어 신호에 따라 비디오 프레임을 자기회귀적으로 생성하지만, 제한된 시간적 문맥 창으로 인해 장기적인 장면 일관성 유지에 어려움을 겪고 이전 환경을 잊는 문제가 발생합니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 기하학 기반의 장기 공간 기억(long-term spatial memory)을 도입하여 비디오 월드 모델의 장기 일관성을 향상시키는 새로운 프레임워크를 제안합니다. 이 프레임워크는 장기 공간 기억에서 정보를 저장하고 검색하는 메커니즘을 포함하며, 3D 기억 메커니즘이 명시적으로 저장된 맞춤형 데이터셋을 활용해 학습 및 평가를 수행합니다. 평가 결과, 제안 방법은 기존 기법 대비 품질, 일관성, 문맥 길이 측면에서 개선된 성능을 보여 장기 일관성 있는 세계 생성에 기여함을 확인하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
새롭게 등장하는 월드 모델은 카메라 움직임, 텍스트 프롬프트 등 다양한 제어 신호에 반응하여 비디오 프레임을 자기회귀적으로 생성합니다. 그러나 제한된 시간적 컨텍스트 윈도우 크기 때문에, 이러한 모델들은 장면을 재방문할 때 일관성을 유지하는 데 어려움을 겪으며 이전에 생성된 환경을 심각하게 망각하는 문제가 발생합니다. 인간 기억 메커니즘에서 영감을 받아, 본 논문에서는 기하학에 기반한 장기 공간 메모리를 통해 비디오 월드 모델의 장기 일관성을 향상시키는 새로운 프레임워크를 제안합니다. 제안하는 프레임워크는 장기 공간 메모리로부터 정보를 저장하고 검색하는 메커니즘을 포함하며, 명시적으로 3D 메모리 메커니즘을 저장하는 월드 모델을 학습 및 평가하기 위한 맞춤형 데이터셋도 구축하였습니다. 평가 결과, 관련 기준 모델 대비 품질, 일관성, 컨텍스트 길이 측면에서 개선된 성능을 보였으며, 이는 장기 일관성 있는 월드 생성으로 나아가는 길을 열어줍니다.
Emerging world models autoregressively generate video frames in response to actions, such as camera movements and text prompts, among other control signals. Due to limited temporal context window sizes, these models often struggle to maintain scene consistency during revisits, leading to severe forgetting of previously generated environments. Inspired by the mechanisms of human memory, we introduce a novel framework to enhancing long-term consistency of video world models through a geometry-grounded long-term spatial memory. Our framework includes mechanisms to store and retrieve information from the long-term spatial memory and we curate custom datasets to train and evaluate world models with explicitly stored 3D memory mechanisms. Our evaluations show improved quality, consistency, and context length compared to relevant baselines, paving the way towards long-term consistent world generation.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
LLM 대리체를 활용한 제로샷 비전 인코더 접목 방법 / Zero-Shot Vision Encoder Grafting via LLM Surrogates
논문 소개
이 연구는 대형 언어 모델(LLM)과 결합된 비전 언어 모델(VLM)의 비용 효율성을 높이기 위한 방법을 제안합니다. 작은 "대리 모델"을 사용하여 비전 인코더를 사전 학습한 후, 이를 대형 LLM에 직접 전이하는 제로샷 가드팅(zero-shot grafting) 기법을 도입하였으며, 이 방식은 전체 모델 학습 비용을 약 45% 절감하면서 성능 향상 또는 유지가 가능합니다. 제안된 방법은 대리 모델이 대형 LLM에 바로 연결될 때, 기존의 전체 디코더 학습과 경쟁하거나 뛰어넘는 성능을 보여줍니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
비전-언어 모델(VLM)은 일반적으로 소형 비전 인코더와 대형 언어 모델(LLM), 예를 들어 Llama-70B를 결합하여 구성되며, 이때 디코더가 학습 시 주요 계산 부담이 됩니다. 비용 절감을 위해 잠재적인 유망 전략은 먼저 소형 언어 모델을 사용하여 비전 인코더를 학습한 후 이를 대형 모델로 이전하는 것입니다. 본 연구에서는 대형 목표 LLM과 동일한 임베딩 공간 및 표현 언어를 공유하는 소형 "서로게이트 모델"을 구축하였으며, 이는 해당 LLM의 얕은 층을 직접 상속받아 만듭니다. 서로게이트로 학습된 비전 인코더는 이후 대형 모델로 바로 이전할 수 있는데, 이를 "제로샷 그라프팅(zero-shot grafting)"이라고 부르며, 전체 크기 목표 LLM에 바로 연결했을 때, 이 그라프된 쌍은 인코더-서로게이트 쌍을 능가하며, 일부 벤치마크에서는 전체 디코더 학습과 견줄 만한 성능을 보여줍니다. 또한, 본 서사 훈련 방식은 Llama-70B를 디코더로 사용할 경우 전체 VLM 학습 비용을 약 45% 절감할 수 있습니다.
Vision language models (VLMs) typically pair a modestly sized vision encoder with a large language model (LLM), e.g., Llama-70B, making the decoder the primary computational burden during training. To reduce costs, a potential promising strategy is to first train the vision encoder using a small language model before transferring it to the large one. We construct small "surrogate models" that share the same embedding space and representation language as the large target LLM by directly inheriting its shallow layers. Vision encoders trained on the surrogate can then be directly transferred to the larger model, a process we call zero-shot grafting -- when plugged directly into the full-size target LLM, the grafted pair surpasses the encoder-surrogate pair and, on some benchmarks, even performs on par with full decoder training with the target LLM. Furthermore, our surrogate training approach reduces overall VLM training costs by ~45% when using Llama-70B as the decoder.
논문 링크
멀티모달 대형 언어모델이 집으로 가는 길을 안내할 수 있을까? 교통지도 기반 세밀한 시각적 추론 평가를 위한 벤치마크 연구 / Can MLLMs Guide Me Home? A Benchmark Study on Fine-Grained Visual Reasoning from Transit Maps
논문 소개
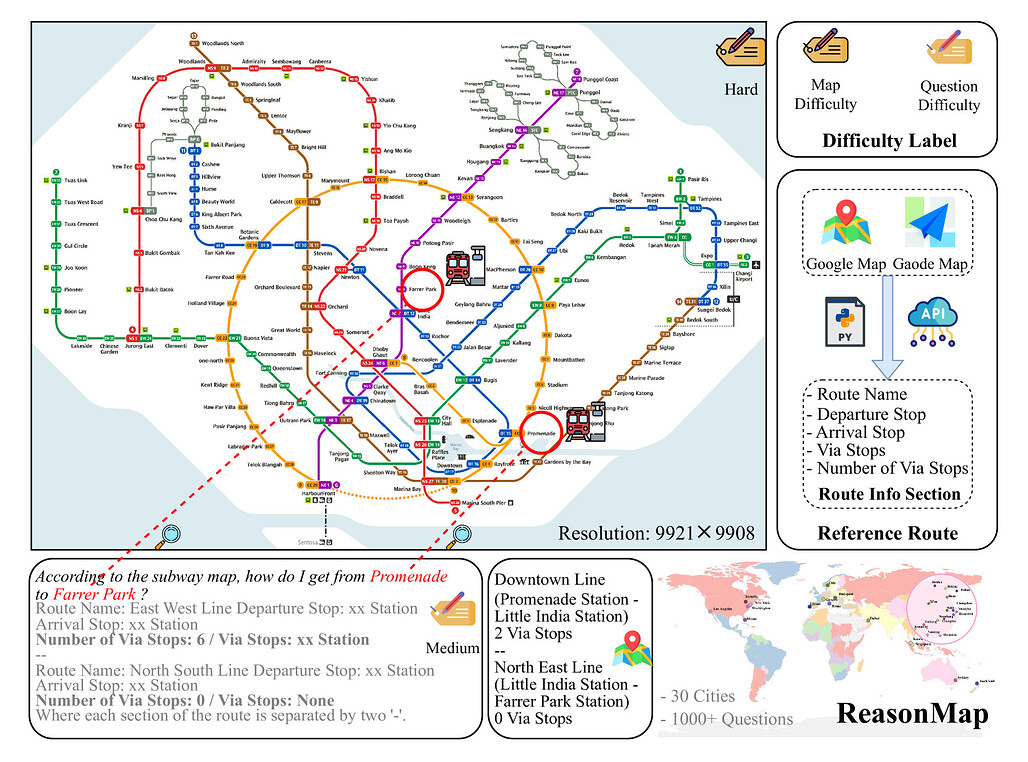
이 연구는 MLLMs(멀티모달 대형 언어 모델)의 정밀한 시각적 이해와 공간 추론 능력을 평가하기 위해 ReasonMap라는 벤치마크를 제시합니다. ReasonMap는 30개 도시의 고해상도 교통 지도와 1,008개의 질문-답변 쌍으로 구성되어 있으며, 두 가지 질문 유형과 세 가지 템플릿을 포함합니다. 평가 결과, 오픈소스 모델에서는 기본 모델이 추론 모델보다 우수한 반면, 폐쇄소스 모델에서는 추론 모델이 더 뛰어난 것으로 나타났으며, 시각적 입력이 마스킹될 경우 성능이 저하되어 정밀한 시각적 인식이 여전히 중요함을 보여줍니다. 이 연구는 시각적 추론 능력의 한계와 오픈소스와 폐쇄소스 모델 간의 차이를 이해하는 데 기여합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 멀티모달 대형 언어 모델(MLLMs)은 의미적 장면 이해와 텍스트-이미지 정렬 등 시각적 작업에서 상당한 발전을 이루었으며, 특히 추론(Reasoning) 변형 모델은 수학과 논리와 같은 복잡한 작업에서 성능을 향상시키고 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 모델들이 세밀한 시각적 이해를 요구하는 추론 작업에서의 능력은 아직 충분히 평가되지 않은 실정입니다. 이에 본 연구에서는 MLLMs의 세밀한 시각적 이해와 공간 추론 능력을 평가하기 위해 ‘ReasonMap’이라는 벤치마크를 제안합니다. ReasonMap은 13개국 30개 도시의 고해상도 교통 지도(Transit Maps)를 포함하며, 총 1,008개의 질문-답변 쌍으로 구성되어 있습니다. 이 질문들은 두 가지 유형과 세 가지 템플릿으로 다양하게 설계되어 있습니다. 또한, 우리는 답변의 정답 여부와 품질을 적절히 평가할 수 있는 이중 단계 평가 파이프라인을 개발하였습니다. 15개 인기 있는 MLLMs(기본 모델과 추론 모델 모두 포함)에 대한 포괄적 평가 결과, 직관에 반하는 흥미로운 패턴이 드러났습니다. 즉, 오픈소스 모델의 경우 기본 모델이 추론 모델보다 우수한 성능을 보인 반면, 폐쇄소스(상용) 모델에서는 추론 모델이 더 뛰어난 성능을 나타냈습니다. 또한, 시각적 입력이 마스킹될 경우 성능이 전반적으로 저하되는 경향이 관찰되었는데, 이는 MLLMs가 일부 질문에 대해 사전 지식을 활용하여 답변할 수는 있지만, 세밀한 시각적 추론 작업에서는 강력한 성능을 위해 진정한 시각적 인지 능력이 여전히 필요하다는 것을 시사합니다. 본 벤치마크 연구는 시각적 추론에 대한 새로운 통찰을 제공하며, 오픈소스와 폐쇄소스 모델 간의 격차를 탐구하는 데 기여할 것으로 기대됩니다.
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently achieved significant progress in visual tasks, including semantic scene understanding and text-image alignment, with reasoning variants enhancing performance on complex tasks involving mathematics and logic. However, their capacity for reasoning tasks involving fine-grained visual understanding remains insufficiently evaluated. To address this gap, we introduce ReasonMap, a benchmark designed to assess the fine-grained visual understanding and spatial reasoning abilities of MLLMs. ReasonMap encompasses high-resolution transit maps from 30 cities across 13 countries and includes 1,008 question-answer pairs spanning two question types and three templates. Furthermore, we design a two-level evaluation pipeline that properly assesses answer correctness and quality. Comprehensive evaluations of 15 popular MLLMs, including both base and reasoning variants, reveal a counterintuitive pattern: among open-source models, base models outperform reasoning ones, while the opposite trend is observed in closed-source models. Additionally, performance generally degrades when visual inputs are masked, indicating that while MLLMs can leverage prior knowledge to answer some questions, fine-grained visual reasoning tasks still require genuine visual perception for strong performance. Our benchmark study offers new insights into visual reasoning and contributes to investigating the gap between open-source and closed-source models.
논문 링크
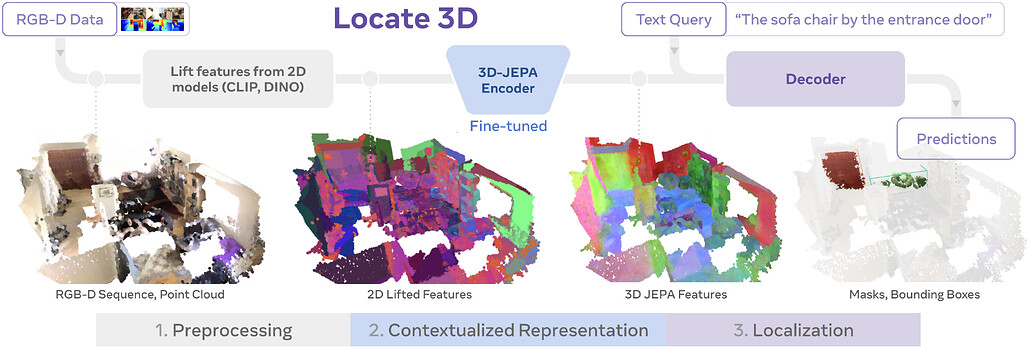
LOCATE 3D: 자기지도 학습 기반 3D 환경 내 객체 위치 추정 및 참조 지시어 이해 / Locate 3D: Real-World Object Localization via Self-Supervised Learning in 3D
논문 소개
LOCATE 3D는 3D 장면 내에서 "소파와 램프 사이의 작은 커피 테이블"과 같은 참조 표현을 통해 객체를 위치시키는 모델입니다. 이 모델은 센서 관측 스트림(포즈가 지정된 RGB-D 프레임)에서 직접 작동하며, 최신 성능을 기록하고 강력한 일반화 능력을 보여줍니다. 핵심 기술인 3D-JEPA는 2D 기반 모델(예: CLIP, DINO)을 활용한 3D 포인트클라우드의 자기지도학습(SSL) 알고리즘으로, 마스킹 예측을 통해 컨텍스트 정보를 학습합니다. 학습된 3D-JEPA 인코더는 언어 조건 디코더와 함께 미세조정되어 3D 마스크와 경계 상자를 예측하며, 이를 지원하는 130K 이상의 주석이 포함된 3D 참조 데이터셋도 제시됩니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
본 논문에서는 "LOCATE 3D"라는 3D 장면 내 객체 위치 추정 모델을 제시합니다. 이 모델은 "소파와 램프 사이에 있는 작은 커피 테이블"과 같은 지시어(referring expressions)를 기반으로 3D 공간 내 객체를 정확히 찾을 수 있습니다. LOCATE 3D는 표준 참조 기반 지상물(Referential Grounding) 벤치마크에서 새로운 최첨단 성능을 달성했으며, 강력한 일반화 능력을 보여줍니다. 특히, LOCATE 3D는 센서 관측 스트림(포즈가 부여된 RGB-D 프레임)에서 직접 작동하여, 로봇이나 증강현실(AR) 기기와의 실제 환경 배포가 가능하도록 설계되었습니다.
이 방법의 핵심은 3D-JEPA라는 새로운 자기지도학습(Self-Supervised Learning, SSL) 알고리즘에 있는데, 이는 센서 포인트 클라우드에 적용할 수 있습니다. 3D-JEPA는 2D 기반 모델(예: CLIP, DINO)을 이용하여 특징화된 3D 포인트 클라우드(포인트클라우드)를 입력으로 받으며, 잠재 공간에서의 마스킹 예측(masked prediction)을 사전 학습 과제로 사용하여 맥락이 반영된 포인트 클라우드 특징의 자기지도학습을 돕습니다. 학습이 완료되면, 3D-JEPA 인코더는 언어 조건이 부여된 디코더와 함께 미세 조정(finetuning)되어, 3D 마스크와 경계 상자(bounding box)를 공동으로 예측하게 됩니다.
또한, 본 연구에서는 3D 참조 지상물 연구를 위한 새로운 데이터셋인 "LOCATE 3D DATASET"을 소개합니다. 이 데이터셋은 여러 촬영 환경에서 130,000개 이상의 주석(annotation)을 포함하며, 다양한 촬영 조건과 환경에서의 일반화 능력을 체계적으로 연구할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다. 이를 통해 모델의 성능 향상과 강인성을 확보하는 데 기여하고자 합니다.
We present LOCATE 3D, a model for localizing objects in 3D scenes from referring expressions like "the small coffee table between the sofa and the lamp." LOCATE 3D sets a new state-of-the-art on standard referential grounding benchmarks and showcases robust generalization capabilities. Notably, LOCATE 3D operates directly on sensor observation streams (posed RGB-D frames), enabling real-world deployment on robots and AR devices. Key to our approach is 3D-JEPA, a novel self-supervised learning (SSL) algorithm applicable to sensor point clouds. It takes as input a 3D pointcloud featurized using 2D foundation models (CLIP, DINO). Subsequently, masked prediction in latent space is employed as a pretext task to aid the self-supervised learning of contextualized pointcloud features. Once trained, the 3D-JEPA encoder is finetuned alongside a language-conditioned decoder to jointly predict 3D masks and bounding boxes. Additionally, we introduce LOCATE 3D DATASET, a new dataset for 3D referential grounding, spanning multiple capture setups with over 130K annotations. This enables a systematic study of generalization capabilities as well as a stronger model.
논문 링크
Llama-Nemotron: 효율적인 추론 성능을 갖춘 오픈 소스 모델 시리즈 / Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models
논문 소개
Llama-Nemotron 시리즈는 뛰어난 추론 능력과 효율성을 갖춘 오픈 소스 이유 모델로, Nano(8B), Super(49B), Ultra(253B) 세 가지 크기로 제공됩니다. 이 모델들은 신경망 구조 검색, 지식 증류, 사전 학습, 그리고 추론 중심의 후처리 과정을 통해 개발되었으며, 표준 채팅과 추론 모드 간 전환이 가능한 동적 추론 토글 기능을 지원합니다. 또한, 이들은 경쟁 모델과 비슷하거나 우수한 성능을 유지하면서도 추론 처리량과 메모리 효율성을 향상시켰으며, 연구와 개발을 위한 다양한 자원과 도구를 공개하고 있습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
본 논문에서는 Llama-Nemotron 시리즈 모델을 소개합니다. 이 시리즈는 다양한 계층의 이종 추론 모델로서 뛰어난 추론 능력, 추론 효율성, 그리고 기업용으로 사용할 수 있는 개방형 라이선스를 제공하는 오픈 프랜차이즈입니다. 이 모델들은 Nano(8B), Super(49B), Ultra(253B)의 세 가지 크기로 제공되며, DeepSeek-R1과 같은 최첨단 추론 모델과 경쟁력 있는 성능을 갖추는 동시에, 추론 처리량과 메모리 효율성 면에서 우수한 성능을 보여줍니다. 본 보고서에서는 이러한 모델들의 학습 과정에 대해 논의하며, 이는 Llama 3 모델을 활용한 신경망 구조 검색(Neural Architecture Search)을 통한 가속화된 추론, 지식 증류(Knowledge Distillation), 그리고 지속적인 사전 학습(Continued Pretraining)을 포함합니다. 이후에는 추론 중심의 후속 학습 단계가 이어지며, 이는 크게 두 부분으로 구성됩니다: 지도 학습을 통한 미세 조정(Supervised Fine-tuning)과 대규모 강화 학습(Large-scale Reinforcement Learning)입니다. Llama-Nemotron 모델은 최초로 공개된 오픈소스 모델로서, 동적 추론 전환 기능(Reasoning Toggle)을 지원하여 사용자가 추론 모드와 일반 채팅 모드 간에 전환할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다. 또한, 오픈 연구를 적극 지원하고 모델 개발을 촉진하기 위해 다음과 같은 자원을 제공합니다: 1. 상업적 사용이 허용된 NVIDIA 오픈 모델 라이선스(NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement) 하에 Llama-Nemotron 추론 모델인 LN-Nano, LN-Super, LN-Ultra를 공개합니다. 2. 전체 후속 학습 데이터셋인 Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset를 공개합니다. 3. 또한, 우리의 학습 코드베이스인 NeMo, NeMo-Aligner, Megatron-LM도 함께 공개합니다.
We introduce the Llama-Nemotron series of models, an open family of heterogeneous reasoning models that deliver exceptional reasoning capabilities, inference efficiency, and an open license for enterprise use. The family comes in three sizes -- Nano (8B), Super (49B), and Ultra (253B) -- and performs competitively with state-of-the-art reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 while offering superior inference throughput and memory efficiency. In this report, we discuss the training procedure for these models, which entails using neural architecture search from Llama 3 models for accelerated inference, knowledge distillation, and continued pretraining, followed by a reasoning-focused post-training stage consisting of two main parts: supervised fine-tuning and large scale reinforcement learning. Llama-Nemotron models are the first open-source models to support a dynamic reasoning toggle, allowing users to switch between standard chat and reasoning modes during inference. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we provide the following resources: 1. We release the Llama-Nemotron reasoning models -- LN-Nano, LN-Super, and LN-Ultra -- under the commercially permissive NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement. 2. We release the complete post-training dataset: Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset. 3. We also release our training codebases: NeMo, NeMo-Aligner, and Megatron-LM.
논문 링크
인공지능 에이전트 프로토콜 현황 및 미래 방향성 분석 / A Survey of AI Agent Protocols
논문 소개
The rapid deployment of large language model (LLM) agents across various industries has highlighted the absence of standardized communication protocols, which hampers collaboration, scalability, and the handling of complex tasks. The paper offers a comprehensive analysis of existing agent protocols, classifying them systematically based on context orientation and purpose, and evaluates their performance in security, scalability, and latency. It also discusses future research directions, emphasizing characteristics such as adaptability, privacy preservation, and support for group interactions, to develop next-generation protocols. This work aims to serve as a practical reference for designing and evaluating robust communication infrastructures for AI agents.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 대형 언어 모델(LLMs, Large Language Models)의 급속한 발전은 고객 서비스, 콘텐츠 생성, 데이터 분석, 심지어 의료 분야를 포함한 다양한 산업 분야에서 LLM 에이전트의 광범위한 활용을 가능하게 하였습니다. 그러나 더 많은 LLM 에이전트가 배포됨에 따라 중요한 문제점이 드러났는데, 바로 이러한 에이전트들이 외부 도구 또는 데이터 소스와 소통할 수 있는 표준화된 방법이 존재하지 않는다는 점입니다. 이러한 표준화된 프로토콜의 부재는 에이전트 간의 협력이나 확장성을 저해하며, 복잡하고 현실적인 과제들을 해결하는 데 한계를 초래합니다. 이에 대한 해결책으로, LLM 에이전트 간의 통신을 위한 통합된 프로토콜이 제시될 수 있습니다. 이는 에이전트와 도구들이 보다 원활하게 상호작용할 수 있게 하고, 협력을 촉진하며, 집단 지능(Collective Intelligence)의 형성을 유도할 수 있습니다. 본 논문에서는 기존 에이전트 프로토콜에 대한 최초의 포괄적 분석을 제공하며, 이를 체계적으로 두 차원으로 분류하는 방식을 제안합니다. 구체적으로는, 맥락 중심 프로토콜(context-oriented)과 에이전트 간 프로토콜(inter-agent protocols), 그리고 범용 프로토콜(general-purpose)과 도메인 특화 프로토콜(domain-specific protocols)을 구별하는 분류입니다. 또한, 이러한 프로토콜들의 성능을 보안(security), 확장성(scalability), 지연 시간(latency) 등 핵심 차원에서 비교 분석하였습니다. 마지막으로, 차세대 에이전트 프로토콜의 미래 방향성을 모색하며, 적응성(adaptability), 프라이버시 보호(privacy preservation), 그룹 기반 상호작용(group-based interaction)과 같은 핵심 연구 과제와 함께, 계층형 아키텍처(layered architectures)와 집단 지능 인프라(collective intelligence infrastructures)로의 트렌드도 함께 살펴보았습니다. 본 연구는 연구자와 엔지니어 모두가 지능형 에이전트의 강력한 통신 인프라를 설계, 평가 또는 통합하는 데 실질적인 참고 자료가 될 것으로 기대됩니다.
The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) has led to the widespread deployment of LLM agents across diverse industries, including customer service, content generation, data analysis, and even healthcare. However, as more LLM agents are deployed, a major issue has emerged: there is no standard way for these agents to communicate with external tools or data sources. This lack of standardized protocols makes it difficult for agents to work together or scale effectively, and it limits their ability to tackle complex, real-world tasks. A unified communication protocol for LLM agents could change this. It would allow agents and tools to interact more smoothly, encourage collaboration, and triggering the formation of collective intelligence. In this paper, we provide the first comprehensive analysis of existing agent protocols, proposing a systematic two-dimensional classification that differentiates context-oriented versus inter-agent protocols and general-purpose versus domain-specific protocols. Additionally, we conduct a comparative performance analysis of these protocols across key dimensions such as security, scalability, and latency. Finally, we explore the future landscape of agent protocols by identifying critical research directions and characteristics necessary for next-generation protocols. These characteristics include adaptability, privacy preservation, and group-based interaction, as well as trends toward layered architectures and collective intelligence infrastructures. We expect this work to serve as a practical reference for both researchers and engineers seeking to design, evaluate, or integrate robust communication infrastructures for intelligent agents.
논문 링크
DoomArena: 진화하는 보안 위협에 대응하는 인공지능 에이전트 테스트 프레임워크 / DoomArena: A framework for Testing AI Agents Against Evolving Security Threats
논문 소개
DoomArena는 AI 에이전트의 보안 평가를 위한 프레임워크로, 플러그인 구조, 상세한 위협 모델링, 모듈화된 설계로 다양한 환경과 공격 기법을 쉽게 통합하고 적용할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다. 이를 통해 최신 웹 및 도구 호출 에이전트의 취약성을 분석한 결과, 여러 공격이 결합될 때 공격 효과가 증대되며, 방어 기법의 한계도 드러났습니다. 특히, 강력한 최신 LLM 기반 방어가 더 효과적임을 확인하였으며, 프레임워크는 새로운 위협 모델과 환경에 유연하게 대응할 수 있습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
본 논문에서는 AI 에이전트의 보안 평가를 위한 프레임워크인 DoomArena를 제시합니다. DoomArena는 세 가지 원칙에 기반하여 설계되었습니다. 첫째, 플러그인(plug-in) 방식의 프레임워크로서, BrowserGym(웹 에이전트용)이나 τ-벤치(툴 호출 에이전트용)와 같은 현실적인 에이전트 프레임워크에 쉽게 통합할 수 있습니다. 둘째, 구성 가능하며 상세한 위협 모델링이 가능하여, 공격 대상이 되는 에이전트의 특정 구성 요소를 지정하거나 공격 대상자를 세밀하게 설정할 수 있습니다. 셋째, 모듈화되어 있어 공격 개발과 에이전트가 배포된 환경의 세부 사항을 분리할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 동일한 공격을 여러 환경에 걸쳐 적용할 수 있습니다.
이 프레임워크의 여러 장점으로는, 새로운 위협 모델과 환경에 쉽게 적응할 수 있는 유연성, 기존에 발표된 여러 공격 기법들을 손쉽게 결합하여 포괄적이고 세밀한 보안 검증이 가능하다는 점, 그리고 다양한 취약점과 성능 간의 트레이드오프를 분석할 수 있다는 점이 있습니다.
우리는 DoomArena를 최신(최신 SOTA) 웹 및 툴 호출 에이전트에 적용하여 여러 흥미로운 결과를 발견하였습니다. 첫째, 최신 에이전트들은 다양한 위협 모델(악의적 사용자 대 악의적 환경)에 대해 서로 다른 수준의 취약성을 보이며, 모든 위협 모델에 대해 우위에 있는 파레토(Pareto) 우위 에이전트는 존재하지 않습니다. 둘째, 여러 공격이 동시에 적용될 경우, 이들이 서로 보완적으로 작용하는 경우가 많습니다. 셋째, Guardrail(가드레일) 모델 기반 방어는 실패하는 반면, 강력한 최신(최신 SOTA) 대형 언어모델(LLM)을 활용한 방어가 더 효과적임을 확인하였습니다.
DoomArena는 이 https URL에서 이용하실 수 있습니다.
We present DoomArena, a security evaluation framework for AI agents. DoomArena is designed on three principles: 1) It is a plug-in framework and integrates easily into realistic agentic frameworks like BrowserGym (for web agents) and \tau-bench (for tool calling agents); 2) It is configurable and allows for detailed threat modeling, allowing configuration of specific components of the agentic framework being attackable, and specifying targets for the attacker; and 3) It is modular and decouples the development of attacks from details of the environment in which the agent is deployed, allowing for the same attacks to be applied across multiple environments. We illustrate several advantages of our framework, including the ability to adapt to new threat models and environments easily, the ability to easily combine several previously published attacks to enable comprehensive and fine-grained security testing, and the ability to analyze trade-offs between various vulnerabilities and performance. We apply DoomArena to state-of-the-art (SOTA) web and tool-calling agents and find a number of surprising results: 1) SOTA agents have varying levels of vulnerability to different threat models (malicious user vs malicious environment), and there is no Pareto dominant agent across all threat models; 2) When multiple attacks are applied to an agent, they often combine constructively; 3) Guardrail model-based defenses seem to fail, while defenses based on powerful SOTA LLMs work better. DoomArena is available at GitHub - ServiceNow/DoomArena: DoomArena is a Framework for Testing AI Agents Against Evolving Security Threats.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
다윈 고델 머신: 자기개선 에이전트의 오픈 엔드 진화 / Darwin Godel Machine: Open-Ended Evolution of Self-Improving Agents
논문 소개
Darwin Godel Machine (DGM)는 자기개선 능력을 갖춘 인공지능으로, 자신의 코드를 반복적으로 수정하며 성능을 향상시킨다. 이 시스템은 진화론과 오픈엔디드 탐색(개방형 탐색) 원리를 기반으로 하여, 다양한 에이전트의 아카이브를 유지하고 새로운 유용한 버전을 생성하는 과정을 통해 여러 경로를 병렬로 탐색한다. 실험 결과, DGM은 코드 편집 도구와 맥락 관리 능력 등에서 성능을 크게 향상시키며, 기존 방법보다 우수한 성과를 보여주었다. 안전장치를 갖춘 상태에서 자기개선과 오픈엔디드 탐색을 통해 무한한 혁신 가능성을 보여주는 중요한 진전이다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
오늘날의 AI 시스템은 인간이 설계한 고정된 구조를 가지며 자율적이고 지속적으로 자체 개선하는 능력이 없습니다. AI의 발전 자체를 자동화하는 것도 가능해지고 있습니다. 안전하게 수행된다면, 이는 AI 개발을 가속화하고 그 혜택을 훨씬 빠르게 누릴 수 있게 할 것입니다. 메타-학습(learning)은 새로운 알고리즘의 발견을 자동화할 수 있지만, 이는 1차적 개선에 제한되며, 적절한 탐색 공간의 인간 설계에 의존합니다. 괴델(Gödel) 기계는 이와 대안이 되는 이론적 모델을 제시했는데, 이는 반복적으로 자신을 수정하는 자기개선형 AI로서, 그 수정이 증명 가능하게 유익한 방식으로 이루어지도록 설계된 시스템입니다. 그러나 대부분의 변경이 순수하게 유익하다는 것을 증명하는 것은 실질적으로 불가능합니다. 본 연구에서는 다윈(Ga) 기계(Darwin Gödel Machine, DGM)를 소개하는데, 이는 자신의 코드를 반복적으로 수정하며(이로써 자신의 코드베이스 수정 능력도 향상시키는) 각 변경 사항을 코딩 벤치마크를 통해 실증적으로 검증하는 자기개선 시스템입니다. 다윈적 진화와 열린 탐색(open-endedness) 연구에서 영감을 받은 DGM은 생성된 코딩 에이전트의 아카이브를 유지하며, 이 아카이브에서 에이전트를 샘플링하고 기반 모델을 활용하여 그 샘플의 흥미로운 새 버전을 생성함으로써 아카이브를 확장합니다. 이러한 열린 탐색은 다양한 고품질 에이전트의 성장하는 트리 구조를 형성하며, 여러 경로를 병렬로 탐색할 수 있게 합니다. 실험적으로, DGM은 코드 편집 도구, 긴 컨텍스트 윈도우 관리, 피어 리뷰 메커니즘 등 코딩 능력을 자동으로 향상시켜, SWE-bench 성능을 20.0%에서 50.0%로, Polyglot 성능을 14.2%에서 30.7%로 향상시켰습니다. 또한, DGM은 자기개선이나 열린 탐색 없이도 기존 방법보다 현저히 우수한 성능을 보여주었습니다. 모든 실험은 샌드박스 환경과 인간 감독 등 안전 조치를 준수하여 수행되었습니다. 본 연구의 DGM은 무한한 혁신으로 이어지는 경로를 스스로 개척하며, 자기개선 능력을 갖춘 AI로 나아가는 중요한 진전입니다.
Today's AI systems have human-designed, fixed architectures and cannot autonomously and continuously improve themselves. The advance of AI could itself be automated. If done safely, that would accelerate AI development and allow us to reap its benefits much sooner. Meta-learning can automate the discovery of novel algorithms, but is limited by first-order improvements and the human design of a suitable search space. The G"odel machine proposed a theoretical alternative: a self-improving AI that repeatedly modifies itself in a provably beneficial manner. Unfortunately, proving that most changes are net beneficial is impossible in practice. We introduce the Darwin G"odel Machine (DGM), a self-improving system that iteratively modifies its own code (thereby also improving its ability to modify its own codebase) and empirically validates each change using coding benchmarks. Inspired by Darwinian evolution and open-endedness research, the DGM maintains an archive of generated coding agents. It grows the archive by sampling an agent from it and using a foundation model to create a new, interesting, version of the sampled agent. This open-ended exploration forms a growing tree of diverse, high-quality agents and allows the parallel exploration of many different paths through the search space. Empirically, the DGM automatically improves its coding capabilities (e.g., better code editing tools, long-context window management, peer-review mechanisms), increasing performance on SWE-bench from 20.0% to 50.0%, and on Polyglot from 14.2% to 30.7%. Furthermore, the DGM significantly outperforms baselines without self-improvement or open-ended exploration. All experiments were done with safety precautions (e.g., sandboxing, human oversight). The DGM is a significant step toward self-improving AI, capable of gathering its own stepping stones along paths that unfold into endless innovation.
논문 링크
![]() 파이토치 한국 사용자 모임
파이토치 한국 사용자 모임![]() 이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일
이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일![]() 로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
![]() 아래
아래![]() 쪽에 좋아요
쪽에 좋아요![]() 를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~
를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~ ![]()