[2025/07/07 ~ 13] 이번 주에 살펴볼 만한 AI/ML 논문 모음
PyTorchKR



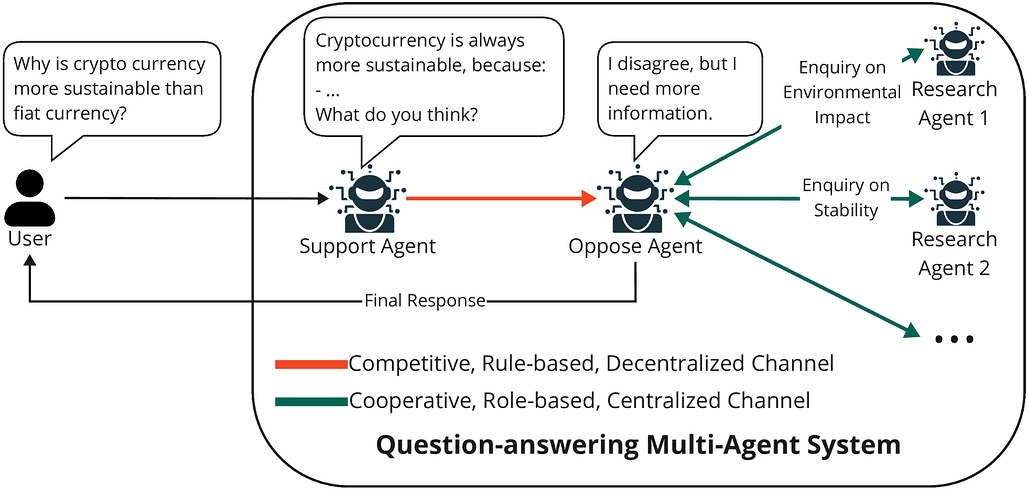
![]() 이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 먼저 LLM을 중심으로 한 다중 에이전트 시스템(MAS)과 에이전트 간 통신 프로토콜에 관한 연구가 두드러집니다. 이는 AI 에이전트들이 단일 모델로서 독립적으로 작동하는 것을 넘어, 서로 협력하고 복잡한 문제를 공동으로 해결하는 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 특히 협업 구조, 역할 분담, 통신 보안 등 다양한 측면에서 체계적인 분석과 프레임워크 제안이 이루어지고 있어, 향후 다중 에이전트 기반 인공지능의 발전 가능성을 시사합니다.
이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 먼저 LLM을 중심으로 한 다중 에이전트 시스템(MAS)과 에이전트 간 통신 프로토콜에 관한 연구가 두드러집니다. 이는 AI 에이전트들이 단일 모델로서 독립적으로 작동하는 것을 넘어, 서로 협력하고 복잡한 문제를 공동으로 해결하는 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 보여줍니다. 특히 협업 구조, 역할 분담, 통신 보안 등 다양한 측면에서 체계적인 분석과 프레임워크 제안이 이루어지고 있어, 향후 다중 에이전트 기반 인공지능의 발전 가능성을 시사합니다.
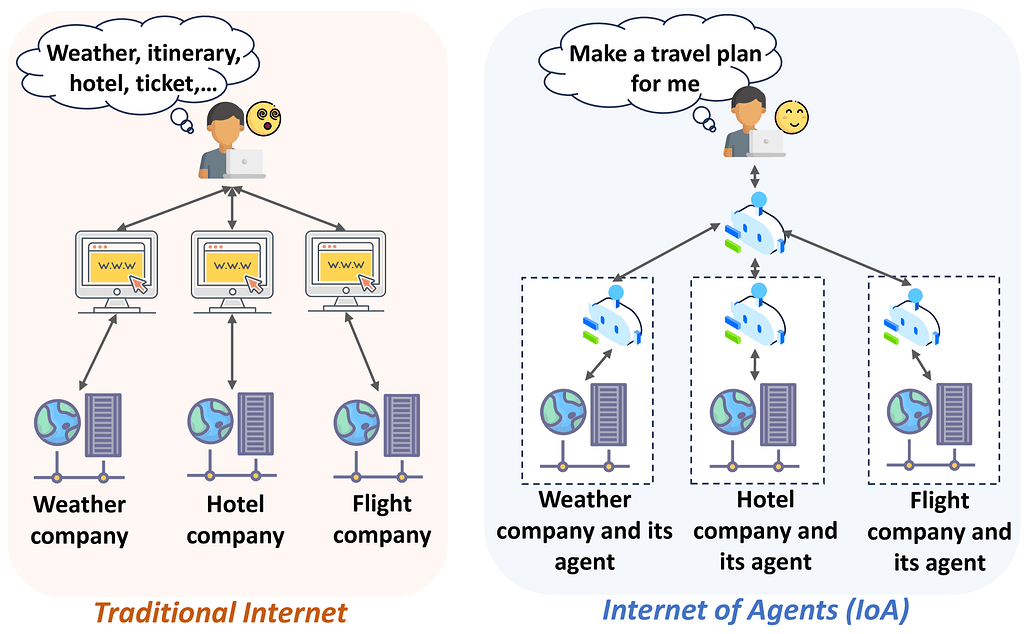
![]() 또한, 물리적 세계와 웹 기반 디지털 정보를 통합하여 에이전트가 보다 현실적이고 복합적인 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 하는 임베디드 웹 에이전트 연구가 주목받고 있습니다. 이를 위해 3D 시뮬레이션 환경과 웹 인터페이스를 결합한 벤치마크가 개발되고, 실제 인간 수준과 비교한 성능 평가가 진행되어 AI의 물리-디지털 융합 능력 향상에 대한 필요성이 강조되고 있습니다.
또한, 물리적 세계와 웹 기반 디지털 정보를 통합하여 에이전트가 보다 현실적이고 복합적인 작업을 수행할 수 있도록 하는 임베디드 웹 에이전트 연구가 주목받고 있습니다. 이를 위해 3D 시뮬레이션 환경과 웹 인터페이스를 결합한 벤치마크가 개발되고, 실제 인간 수준과 비교한 성능 평가가 진행되어 AI의 물리-디지털 융합 능력 향상에 대한 필요성이 강조되고 있습니다.
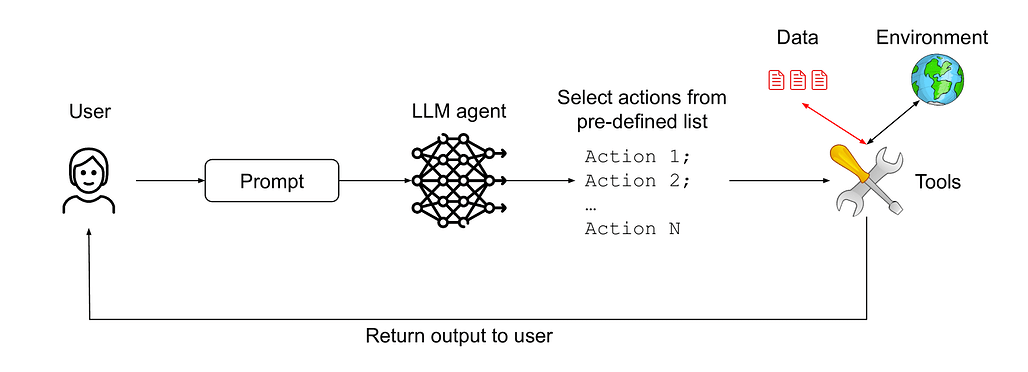
![]() 마지막으로, AI 에이전트가 자연어 입력을 처리하는 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 보안 취약점, 특히 프롬프트 인젝션 공격에 대응하기 위한 설계 패턴과 방어책 연구가 활발합니다. 이는 AI 에이전트가 점점 더 다양한 도구와 민감한 정보를 다루게 되면서 보안 위협이 현실적인 문제로 대두되고 있음을 반영합니다. 따라서 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 AI 시스템 구축을 위한 기초 연구와 실제 적용 사례가 함께 제시되고 있어, 보안 분야의 중요성이 더욱 커지고 있음을 알 수 있습니다.
마지막으로, AI 에이전트가 자연어 입력을 처리하는 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 보안 취약점, 특히 프롬프트 인젝션 공격에 대응하기 위한 설계 패턴과 방어책 연구가 활발합니다. 이는 AI 에이전트가 점점 더 다양한 도구와 민감한 정보를 다루게 되면서 보안 위협이 현실적인 문제로 대두되고 있음을 반영합니다. 따라서 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 AI 시스템 구축을 위한 기초 연구와 실제 적용 사례가 함께 제시되고 있어, 보안 분야의 중요성이 더욱 커지고 있음을 알 수 있습니다.
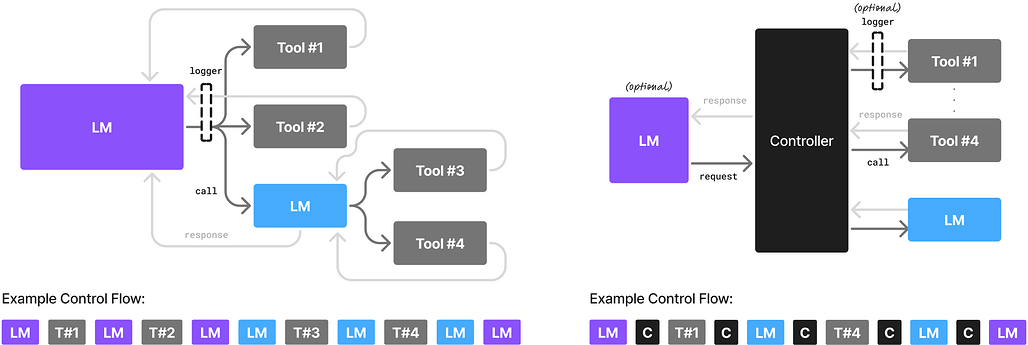
현실-디지털 융합 에이전트를 위한 구현형 웹 에이전트 / Embodied Web Agents: Bridging Physical-Digital Realms for Integrated Agent Intelligence
논문 소개
현재 AI 에이전트는 주로 디지털 정보 탐색과 물리적 환경 상호작용 중 하나에 집중되어 있어, 두 영역을 통합한 복합적인 문제 해결에 한계가 있습니다. Embodied Web Agents는 이러한 물리적 체현(embodiment)과 웹 기반 대규모 추론을 유기적으로 연결하는 새로운 패러다임을 제안합니다. 이를 위해 3D 실내외 환경과 웹 인터페이스를 통합한 시뮬레이션 플랫폼과 다양한 실제 과제를 포함하는 벤치마크를 개발하여, 물리적·디지털 영역 간 협업 능력을 체계적으로 평가합니다. 실험 결과는 최신 AI 기술과 인간 능력 간 큰 성능 격차를 보여주며, 체현 인지와 웹 지식 접근의 융합 분야에서 도전과 기회를 동시에 제시합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
오늘날 AI 에이전트는 대부분 분리되어 운영되고 있습니다. 이들은 온라인에서 획득한 방대한 디지털 정보와 지식을 검색하고 추론하거나, 혹은 구현된 지각, 계획 및 행동을 통해 물리적 세계와 상호작용하지만, 두 가지를 동시에 수행하는 경우는 드뭅니다. 이러한 분리는 온라인 레시피를 활용한 요리, 동적 지도 데이터를 이용한 내비게이션, 웹 지식을 활용한 실제 랜드마크 해석 등 물리적 지능과 디지털 지능의 통합이 필요한 과제 해결 능력을 제한합니다. 본 논문에서는 구현된 지능과 웹 규모 추론을 유기적으로 연결하는 새로운 AI 에이전트 패러다임인 Embodied Web Agents를 제안합니다. 이를 실현하기 위해, 현실감 있는 3D 실내외 환경과 기능적인 웹 인터페이스를 긴밀히 통합한 통합 시뮬레이션 플랫폼인 Embodied Web Agents 과제 환경을 먼저 개발하였습니다. 이 플랫폼을 기반으로 요리, 내비게이션, 쇼핑, 관광, 지리 위치 확인 등 물리적 영역과 디지털 영역 간의 협력적 추론을 요구하는 다양한 과제를 포함하는 Embodied Web Agents 벤치마크를 구축 및 공개합니다. 실험 결과는 최신 AI 시스템과 인간 능력 간에 상당한 성능 격차가 존재함을 보여주며, 구현된 인지와 웹 규모 지식 접근의 교차점에서 도전과 기회를 동시에 제시합니다. 모든 데이터셋, 코드 및 웹사이트는 프로젝트 페이지(https://embodied-web-agent.github.io/)에서 공개되어 있습니다.
AI agents today are mostly siloed - they either retrieve and reason over vast amount of digital information and knowledge obtained online; or interact with the physical world through embodied perception, planning and action - but rarely both. This separation limits their ability to solve tasks that require integrated physical and digital intelligence, such as cooking from online recipes, navigating with dynamic map data, or interpreting real-world landmarks using web knowledge. We introduce Embodied Web Agents, a novel paradigm for AI agents that fluidly bridge embodiment and web-scale reasoning. To operationalize this concept, we first develop the Embodied Web Agents task environments, a unified simulation platform that tightly integrates realistic 3D indoor and outdoor environments with functional web interfaces. Building upon this platform, we construct and release the Embodied Web Agents Benchmark, which encompasses a diverse suite of tasks including cooking, navigation, shopping, tourism, and geolocation - all requiring coordinated reasoning across physical and digital realms for systematic assessment of cross-domain intelligence. Experimental results reveal significant performance gaps between state-of-the-art AI systems and human capabilities, establishing both challenges and opportunities at the intersection of embodied cognition and web-scale knowledge access. All datasets, codes and websites are publicly available at our project page https://embodied-web-agent.github.io/.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
프롬프트 인젝션 방어를 위한 LLM 에이전트 설계 패턴 / Design Patterns for Securing LLM Agents against Prompt Injections
논문 소개
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 기반으로 한 AI 에이전트가 다양한 작업을 수행함에 따라, 프롬프트 인젝션 공격과 같은 보안 위협이 중요한 문제로 대두되고 있습니다. 특히 도구 접근 권한이 부여되거나 민감한 정보를 다루는 경우 이러한 공격은 더욱 위험합니다. 본 연구에서는 프롬프트 인젝션에 대해 증명 가능한 저항성을 갖는 AI 에이전트 설계를 위한 원칙적 디자인 패턴을 제안하고, 각 패턴의 효용성과 보안성 간의 상충관계를 체계적으로 분석합니다. 또한 실제 사례 연구를 통해 제안한 패턴들의 실용성을 입증합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 언어 모델(LLM) 기반 AI 에이전트가 점점 더 다재다능해지고 다양한 과제를 수행할 수 있게 됨에 따라, 이들의 보안을 보장하는 것이 중요한 과제로 부상하고 있습니다. 가장 시급한 위협 중 하나는 프롬프트 인젝션 공격으로, 이는 자연어 입력에 대한 에이전트의 내성을 악용하는 공격이며, 특히 에이전트가 도구 접근 권한을 부여받거나 민감한 정보를 처리할 때 매우 위험합니다. 본 연구에서는 프롬프트 인젝션에 대해 증명 가능한 저항성을 갖는 AI 에이전트를 구축하기 위한 원칙 기반 설계 패턴 세트를 제안합니다. 우리는 이들 패턴을 체계적으로 분석하고, 유용성과 보안 측면에서의 상충관계를 논의하며, 일련의 사례 연구를 통해 실제 적용 가능성을 입증합니다.
As AI agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly versatile and capable of addressing a broad spectrum of tasks, ensuring their security has become a critical challenge. Among the most pressing threats are prompt injection attacks, which exploit the agent's resilience on natural language inputs -- an especially dangerous threat when agents are granted tool access or handle sensitive information. In this work, we propose a set of principled design patterns for building AI agents with provable resistance to prompt injection. We systematically analyze these patterns, discuss their trade-offs in terms of utility and security, and illustrate their real-world applicability through a series of case studies.
논문 링크
LLM 기반 다중 에이전트 협업 메커니즘 서베이 / Multi-Agent Collaboration Mechanisms: A Survey of LLMs
논문 소개
최근 대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 기반으로 한 다중 에이전트 시스템(MAS)은 여러 에이전트가 협력하여 복잡한 문제를 해결하는 협업 중심의 접근법으로 발전하고 있습니다. 본 연구는 MAS의 협업 메커니즘을 행위자, 유형(협력, 경쟁, 협경쟁), 구조(동료 간, 중앙집중형, 분산형), 전략(역할 기반, 모델 기반), 그리고 조정 프로토콜 등 주요 차원으로 체계화한 확장 가능한 프레임워크를 제안합니다. 다양한 분야에서 MAS의 적용 사례를 검토하며, 5G/6G 네트워크, 산업 5.0, 질의응답, 사회·문화적 환경 등에서의 활용 가능성과 영향력을 분석하였습니다. 마지막으로, MAS 발전을 위한 핵심 교훈과 미해결 과제, 향후 연구 방향을 제시하여 인공 집단 지능(artificial collective intelligence) 구현에 기여하고자 합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 발전과 함께, 에이전트 기반 AI는 실제 응용 분야에서 획기적인 성과를 이루고 있으며, 여러 LLM 기반 에이전트가 협력하여 인지, 학습, 추론 및 행동하는 방향으로 나아가고 있습니다. 이러한 LLM 기반 다중 에이전트 시스템(MAS)은 지능형 에이전트 집단이 대규모로 복잡한 과제를 협력적으로 해결할 수 있도록 하며, 개별 모델에서 협업 중심 접근법으로의 전환을 가능하게 합니다. 본 논문은 MAS의 협업 측면에 대한 광범위한 서베이를 제공하며, 향후 연구를 안내할 수 있는 확장 가능한 프레임워크를 제안합니다. 제안된 프레임워크는 협업 메커니즘을 주요 차원별로 특성화하는데, 여기에는 행위자(참여 에이전트), 유형(예: 협력, 경쟁, 또는 협경쟁), 구조(예: 피어 투 피어, 중앙집중식, 분산식), 전략(예: 역할 기반 또는 모델 기반), 그리고 조정 프로토콜이 포함됩니다. 기존 방법론에 대한 검토를 통해 본 연구 결과는 복잡하고 실제적인 사용 사례에 대해 보다 지능적이고 협력적인 LLM 기반 MAS 발전을 위한 기초를 제공합니다. 또한 5G/6G 네트워크, 인더스트리 5.0, 질문 응답, 사회 및 문화 환경 등 다양한 분야에서 MAS의 응용 사례를 조사하여 그 광범위한 채택과 영향력을 입증합니다. 마지막으로, 본 논문은 MAS가 인공 집단 지능으로 나아가기 위한 주요 교훈, 미해결 과제 및 잠재적 연구 방향을 제시합니다.
With recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs), Agentic AI has become phenomenal in real-world applications, moving toward multiple LLM-based agents to perceive, learn, reason, and act collaboratively. These LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems (MASs) enable groups of intelligent agents to coordinate and solve complex tasks collectively at scale, transitioning from isolated models to collaboration-centric approaches. This work provides an extensive survey of the collaborative aspect of MASs and introduces an extensible framework to guide future research. Our framework characterizes collaboration mechanisms based on key dimensions: actors (agents involved), types (e.g., cooperation, competition, or coopetition), structures (e.g., peer-to-peer, centralized, or distributed), strategies (e.g., role-based or model-based), and coordination protocols. Through a review of existing methodologies, our findings serve as a foundation for demystifying and advancing LLM-based MASs toward more intelligent and collaborative solutions for complex, real-world use cases. In addition, various applications of MASs across diverse domains, including 5G/6G networks, Industry 5.0, question answering, and social and cultural settings, are also investigated, demonstrating their wider adoption and broader impacts. Finally, we identify key lessons learned, open challenges, and potential research directions of MASs towards artificial collective intelligence.
논문 링크
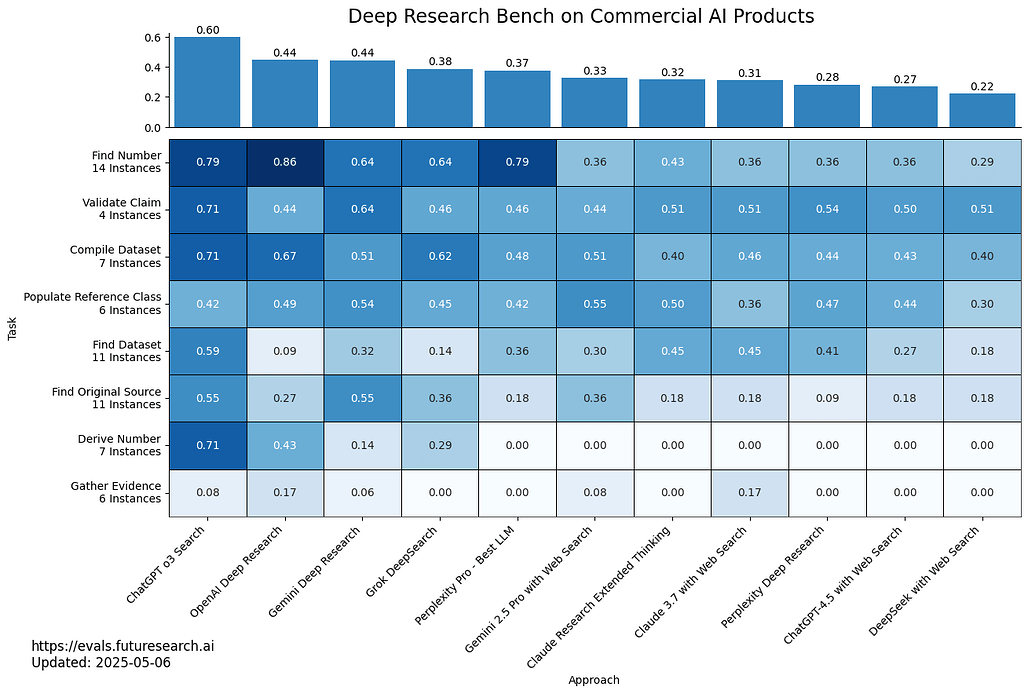
딥 리서치 벤치: AI 웹 리서치 에이전트 평가 플랫폼 / Deep Research Bench: Evaluating AI Web Research Agents
논문 소개
현대 AI에서 LLM(대형 언어 모델) 기반 웹 검색 기능을 활용한 대화형 에이전트의 성능 평가가 부족한 점을 보완하기 위해, 다양한 난이도와 8개 범주로 구성된 89개의 다단계 웹 연구 과제를 포함하는 Deep Research Bench를 제안합니다. 고정된 웹 페이지 데이터셋을 활용하는 "RetroSearch" 환경을 제공하여, 실시간 웹 기반 에이전트와 유사한 성능을 보이는 오프라인 평가를 가능하게 하였습니다. 주요 LLM 모델과 사고형(thinking) 모델을 포함한 다양한 에이전트를 벤치마킹할 수 있도록 도구와 평가 체계를 구축하였으며, 환각(hallucination), 도구 사용, 정보 망각 등 여러 측면에서 자동화된 평가를 수행합니다. 또한, 주요 웹 연구 제품들의 성능을 비교 분석한 결과를 공개 리더보드를 통해 제공하고 있습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
현대 AI의 가장 일반적인 활용 사례 중 하나는 웹 검색이 가능한 LLM 채팅입니다. 그러나 지속적으로 변화하는 웹 환경을 통제한 상태에서 웹 리서치 에이전트의 품질을 직접 평가한 연구는 존재하지 않습니다. 본 논문에서는 8개의 다양한 작업 카테고리에 걸쳐 난이도가 상이한 89개의 다단계 웹 리서치 작업 인스턴스로 구성된 Deep Research Bench를 소개하며, 답안은 숙련된 인간 전문가들이 신중하게 작성하였습니다. 대규모 고정 스크랩 웹 페이지 집합을 포함하는 "RetroSearch" 환경을 제공하고, 오프라인 "RetroSearch" 에이전트가 "실시간 웹(live web)" 에이전트와 유사한 성능을 보임을 입증하여 모델의 장기적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 평가를 가능하게 합니다. 또한 o3, Gemini 2.5 Pro와 같은 "사고하는(thinking)" 모델을 포함하여 주요 LLM의 출시 시점에 맞춰 벤치마크할 수 있는 견고한 에이전트 도구 및 스캐폴딩을 제공합니다. 긴 에이전트 실행 기록에 대한 자동화된 평가를 통해 환각(hallucination), 도구 사용, 망각 등의 진행 상황을 시간 경과에 따라 보고합니다. 마지막으로 "Deep Research", "Deep Search", "Search", "Research" 브랜드의 주요 웹 리서치 제품들을 평가하였습니다. 결과는 https://drb.futuresearch.ai/ 에 공개된 리더보드에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
Amongst the most common use cases of modern AI is LLM chat with web search enabled. However, no direct evaluations of the quality of web research agents exist that control for the continually-changing web. We introduce Deep Research Bench, consisting of 89 multi-step web research task instances of varying difficulty across 8 diverse task categories, with the answers carefully worked out by skilled humans. We provide a "RetroSearch" environment with a large frozen set of scraped web pages, and demonstrate that offline "RetroSearch" agents perform comparably to "live web" agents, enabling reliable evaluations of models over time. We provide robust agent tooling and scaffolding to benchmark major LLMs as they are released, including "thinking" models like o3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro. We include automated evaluations of the lengthy agent traces to report progress over time in hallucinations, tool use, and forgetting. Finally, we evaluate the major web research products branded as "Deep Research", "Deep Search", "Search", or "Research." Results are available on a public leaderboard at https://drb.futuresearch.ai/.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
LLM 기반 AI 에이전트 통신 서베이: 프로토콜, 보안 위험 및 방어 대책 / A Survey of LLM-Driven AI Agent Communication: Protocols, Security Risks, and Defense Countermeasures
논문 소개
최근 대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 기반으로 한 AI 에이전트들은 뛰어난 지능과 적응력을 바탕으로 인간의 생산과 생활 방식을 빠르게 변화시키고 있습니다. 이러한 에이전트들은 더 이상 독립적으로 작동하지 않고, 다른 에이전트나 도구와 소통하며 복잡한 작업을 공동 수행하는 방향으로 진화하고 있습니다. 본 논문은 에이전트 간 통신을 사용자-에이전트 상호작용, 에이전트 간 통신, 에이전트-환경 통신의 세 단계로 구분하고, 각 단계별 프로토콜과 보안 위험을 분석하며 이에 대한 방어 대책을 제시합니다. 또한, 향후 연구 과제와 발전 방향을 논의하여 에이전트 통신 보안 분야의 이해와 발전에 기여하고자 합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 몇 년간, 대형 언어 모델(LLM) 기반 AI 에이전트는 전례 없는 지능, 유연성 및 적응력을 보여주며 인간의 생산과 생활 방식을 빠르게 변화시키고 있습니다. 현재 에이전트는 새로운 진화 단계를 맞이하고 있습니다. 이들은 더 이상 LLM처럼 고립된 섬으로 작동하지 않고, 다른 에이전트 및 도구와 같은 다양한 외부 주체들과 소통하여 보다 복잡한 작업을 집단적으로 수행하기 시작했습니다. 이러한 흐름 속에서 에이전트 간 통신은 미래 AI 생태계의 근간으로 간주되며, 최근 몇 개월 동안 Anthropic의 MCP, Google의 A2A와 같은 관련 통신 프로토콜 설계가 여러 조직에서 집중적으로 이루어지고 있습니다. 그러나 이 새로운 분야는 현실 세계 시나리오에 심각한 피해를 초래할 수 있는 중대한 보안 위험을 내포하고 있습니다. 연구자들이 이 유망한 주제를 신속히 파악하고 미래 에이전트 통신 발전에 기여할 수 있도록, 본 논문은 에이전트 통신 보안에 관한 포괄적인 서베이를 제공합니다. 구체적으로, 먼저 에이전트 통신에 대한 명확한 정의를 제시하고, 에이전트 통신의 전체 생명주기를 사용자-에이전트 상호작용, 에이전트-에이전트 통신, 에이전트-환경 통신의 세 단계로 분류합니다. 다음으로 각 통신 단계별로 관련 프로토콜을 분석하고, 통신 특성에 따라 보안 위험을 상세히 고찰합니다. 이어서 각 위험에 대한 가능한 방어 대책을 요약하고 전망합니다. 마지막으로, 이 유망한 연구 분야에서의 미해결 문제와 향후 연구 방향을 논의합니다.
In recent years, Large-Language-Model-driven AI agents have exhibited unprecedented intelligence, flexibility, and adaptability, and are rapidly changing human production and lifestyle. Nowadays, agents are undergoing a new round of evolution. They no longer act as an isolated island like LLMs. Instead, they start to communicate with diverse external entities, such as other agents and tools, to collectively perform more complex tasks. Under this trend, agent communication is regarded as a foundational pillar of the future AI ecosystem, and many organizations intensively begin to design related communication protocols (e.g., Anthropic's MCP and Google's A2A) within the recent few months. However, this new field exposes significant security hazard, which can cause severe damage to real-world scenarios. To help researchers to quickly figure out this promising topic and benefit the future agent communication development, this paper presents a comprehensive survey of agent communication security. More precisely, we first present a clear definition of agent communication and categorize the entire lifecyle of agent communication into three stages: user-agent interaction, agent-agent communication, and agent-environment communication. Next, for each communication phase, we dissect related protocols and analyze its security risks according to the communication characteristics. Then, we summarize and outlook on the possible defense countermeasures for each risk. Finally, we discuss open issues and future directions in this promising research field.
논문 링크
소규모 언어 모델이 주도하는 에이전트 AI의 미래 / Small Language Models are the Future of Agentic AI
논문 소개
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)은 다양한 작업에서 인간에 가까운 성능과 일반 대화 능력으로 주목받지만, 에이전트 AI 시스템에서는 반복적이고 특화된 소수 작업 수행에 적합한 소규모 언어 모델(SLM)이 더 효율적이고 경제적임을 제시합니다. SLM은 현재 수준의 성능과 에이전트 시스템 구조, 배포 비용 측면에서 충분한 역량을 갖추고 있으며, 범용 대화 능력이 필요한 경우에는 여러 모델을 조합하는 이종 에이전트 시스템이 적합하다고 주장합니다. 또한 SLM 도입의 장애물과 LLM에서 SLM으로 전환하는 알고리즘을 제안하며, AI 자원 활용의 효율성 증대와 비용 절감을 위한 논의를 촉진하고자 합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)은 다양한 과제에서 인간에 가까운 성능을 보이고 일반적인 대화를 수행하는 능력으로 높이 평가받고 있습니다. 그러나 에이전트형 AI 시스템의 부상은 언어 모델이 소수의 전문화된 작업을 반복적이고 거의 변동 없이 수행하는 다수의 응용 분야를 열어가고 있습니다. 본 논문에서는 소규모 언어 모델(SLM)이 충분한 성능을 갖추고 있으며, 본질적으로 에이전트형 시스템에 더 적합하고, 경제성 측면에서도 필수적으로 유리하여 에이전트형 AI의 미래임을 제시합니다. 우리의 주장은 SLM이 현재 보여주는 능력 수준, 에이전트형 시스템의 일반적인 아키텍처, 그리고 언어 모델 배포의 경제성에 근거합니다. 또한, 범용 대화 능력이 필수적인 상황에서는 이종 에이전트 시스템(즉, 여러 다른 모델을 호출하는 에이전트)이 자연스러운 선택임을 논의합니다. 우리는 SLM이 에이전트형 시스템에 도입되는 데 있어 잠재적 장벽을 검토하고, 일반적인 LLM에서 SLM으로의 에이전트 변환 알고리즘을 개략적으로 제시합니다. 본 입장은 가치 진술로서, LLM에서 SLM으로의 부분적 전환만으로도 AI 에이전트 산업에 미칠 운영적·경제적 영향의 중요성을 강조합니다. 우리는 AI 자원의 효과적 활용에 대한 논의를 촉진하고, 현재 AI 비용 절감 노력을 진전시키고자 합니다. 본 입장에 대한 기여와 비판을 모두 환영하며, 관련 모든 소통은 Small Language Models are the Future of Agentic AI 에 공개할 것을 약속드립니다.
Large language models (LLMs) are often praised for exhibiting near-human performance on a wide range of tasks and valued for their ability to hold a general conversation. The rise of agentic AI systems is, however, ushering in a mass of applications in which language models perform a small number of specialized tasks repetitively and with little variation. Here we lay out the position that small language models (SLMs) are sufficiently powerful, inherently more suitable, and necessarily more economical for many invocations in agentic systems, and are therefore the future of agentic AI. Our argumentation is grounded in the current level of capabilities exhibited by SLMs, the common architectures of agentic systems, and the economy of LM deployment. We further argue that in situations where general-purpose conversational abilities are essential, heterogeneous agentic systems (i.e., agents invoking multiple different models) are the natural choice. We discuss the potential barriers for the adoption of SLMs in agentic systems and outline a general LLM-to-SLM agent conversion algorithm. Our position, formulated as a value statement, highlights the significance of the operational and economic impact even a partial shift from LLMs to SLMs is to have on the AI agent industry. We aim to stimulate the discussion on the effective use of AI resources and hope to advance the efforts to lower the costs of AI of the present day. Calling for both contributions to and critique of our position, we commit to publishing all such correspondence at Small Language Models are the Future of Agentic AI.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
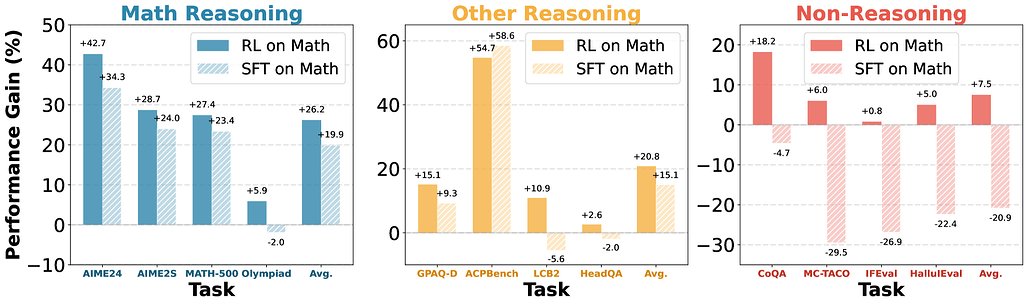
수학적 추론이 LLM의 일반 능력 향상에 미치는 영향과 추론 전이 가능성 분석 / Does Math Reasoning Improve General LLM Capabilities? Understanding Transferability of LLM Reasoning
논문 소개
수학 추론 능력 향상이 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 전반적인 문제 해결 능력으로 확장되는지 여부를 평가하기 위해 20개 이상의 오픈 소스 추론 튜닝 모델을 다양한 분야에서 테스트하였습니다. 대부분의 모델은 수학 분야에서 뛰어난 성과를 보였으나, 다른 도메인으로의 전이 능력은 제한적임을 확인하였습니다. 특히, 강화학습(RL) 기반 튜닝은 다양한 도메인에서 일반화 성능을 유지하는 반면, 지도학습 기반 미세조정(SFT)은 일반 능력 저하와 표현 공간 및 출력 분포의 큰 변화를 유발하는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이러한 결과는 추론 모델 개선을 위한 후처리 방법론, 특히 SFT 데이터 활용에 대한 재고가 필요함을 시사합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
수학 추론은 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 발전을 대표하는 분야로, 새로운 모델들이 MATH 및 AIME와 같은 벤치마크에서 인간 수준의 성능을 빠르게 뛰어넘고 있습니다. 그러나 수학 리더보드의 성과가 주마다 향상됨에 따라, 이러한 향상이 광범위한 문제 해결 능력을 반영하는지 아니면 단지 좁은 범위의 과적합인지에 대한 의문이 제기됩니다. 이 질문에 답하기 위해, 우리는 수학, 과학적 질의응답(QA), 에이전트 계획, 코딩, 그리고 표준 명령 수행을 포함한 다양한 과제에 대해 20개 이상의 오픈 웨이트 추론 튜닝 모델을 평가하였습니다. 놀랍게도, 수학에서 성공한 대부분의 모델이 다른 도메인으로의 성과 이전에는 실패하는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이 현상을 엄밀히 연구하기 위해, 우리는 수학 전용 데이터와 서로 다른 튜닝 방법을 사용하여 Qwen3-14B 모델에 대한 통제된 실험을 수행했습니다. 그 결과, 강화학습(RL) 튜닝 모델은 도메인 간 일반화가 우수한 반면, 감독학습 미세조정(SFT) 튜닝 모델은 종종 일반적 역량을 상실하는 경향이 있음을 발견했습니다. 잠재 공간 표현과 토큰 공간 분포 변화 분석을 통해, SFT가 상당한 표현 및 출력 변이를 유발하는 반면, RL은 일반 도메인 구조를 보존함을 확인했습니다. 본 연구 결과는 추론 모델 발전을 위해 SFT 증류 데이터에 의존하는 기존의 사후 학습 방식에 대해 재고할 필요가 있음을 시사합니다.
Math reasoning has become the poster child of progress in large language models (LLMs), with new models rapidly surpassing human-level performance on benchmarks like MATH and AIME. But as math leaderboards improve week by week, it is worth asking: do these gains reflect broader problem-solving ability or just narrow overfitting? To answer this question, we evaluate over 20 open-weight reasoning-tuned models across a broad suite of tasks, including math, scientific QA, agent planning, coding, and standard instruction-following. We surprisingly find that most models that succeed in math fail to transfer their gains to other domains. To rigorously study this phenomenon, we conduct controlled experiments on Qwen3-14B models using math-only data but different tuning methods. We find that reinforcement learning (RL)-tuned models generalize well across domains, while supervised fine-tuning (SFT)-tuned models often forget general capabilities. Latent-space representation and token-space distribution shift analyses reveal that SFT induces substantial representation and output drift, while RL preserves general-domain structure. Our results suggest a need to rethink standard post-training recipes, particularly the reliance on SFT-distilled data for advancing reasoning models.
논문 링크
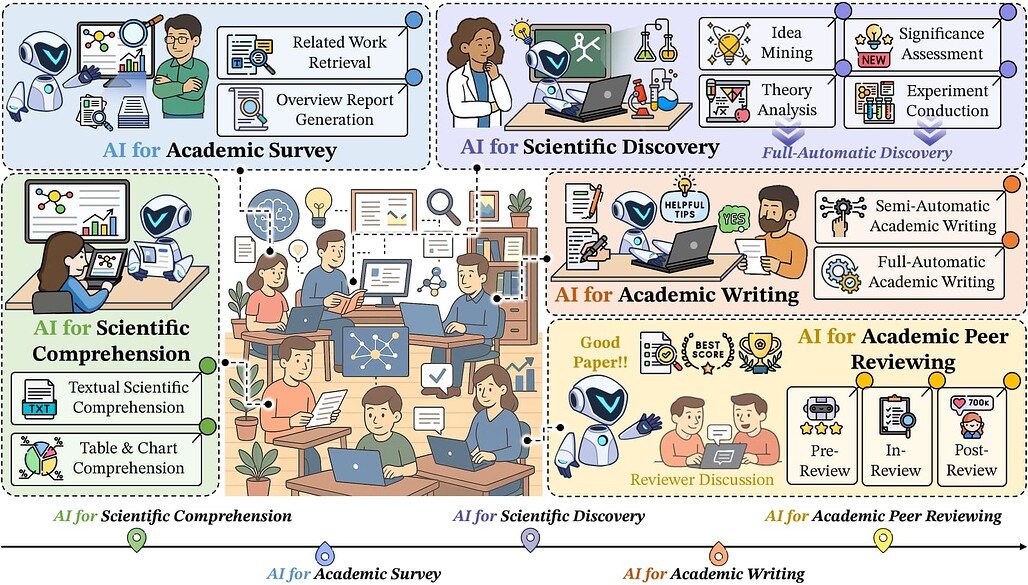
AI4Research: 과학 연구를 위한 인공지능 서베이 / AI4Research: A Survey of Artificial Intelligence for Scientific Research
논문 소개
최근 대규모 언어 모델(LLM) 기반 인공지능(AI)이 논리 추론과 실험 코드 작성 등 복잡한 과학 연구 분야에서 뛰어난 성과를 보이고 있습니다. 이러한 발전을 바탕으로 AI가 다양한 과학 분야에서 자율적으로 연구 과정을 수행할 수 있도록 하는 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있으나, AI4Research 분야에 대한 체계적인 종합 조사는 부족한 실정입니다. 본 연구는 AI4Research의 다섯 가지 주요 과제를 분류하는 체계적 분류법을 제시하고, 자동화된 실험의 엄밀성과 확장성, 사회적 영향 등 향후 연구 방향을 제안합니다. 또한, 다학제적 응용 사례와 데이터, 도구 등 풍부한 자원을 정리하여 연구자들이 신속히 활용할 수 있도록 지원하고자 합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 인공지능(AI), 특히 OpenAI-o1 및 DeepSeek-R1과 같은 대형 언어 모델(LLM) 분야에서의 발전은 논리적 추론 및 실험적 코딩과 같은 복잡한 영역에서 뛰어난 역량을 보여주고 있습니다. 이러한 발전에 힘입어, 다수의 연구들이 과학 연구 맥락에서 혁신 프로세스에 AI를 적용하는 방안을 탐구해왔습니다. 이들 AI 기술은 주로 다양한 과학 분야에서 자율적으로 연구 과정을 수행할 수 있는 시스템 개발을 목표로 하고 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 중요한 진전에도 불구하고, AI for Research(AI4Research)에 관한 포괄적인 서베이 논문이 부재하여 해당 분야에 대한 이해와 추가 발전이 저해되고 있습니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 본 논문에서는 AI4Research에 대한 체계적인 서베이와 통합적 관점을 제시합니다. 구체적으로, 본 연구의 주요 기여는 다음과 같습니다: (1) 체계적 분류체계: AI4Research의 다섯 가지 주류 과제를 분류하는 체계적 분류체계를 처음으로 도입하였습니다. (2) 새로운 연구 영역: 자동화된 실험의 엄밀성과 확장성, 그리고 사회적 영향에 중점을 두어 주요 연구 공백을 식별하고 유망한 미래 연구 방향을 제시하였습니다. (3) 풍부한 응용 및 자원: 관련 다학제적 응용, 데이터 코퍼스, 도구 등 다양한 자원을 종합적으로 수집하였습니다. 본 연구가 연구 커뮤니티에 이러한 자원에 대한 신속한 접근을 제공하고 AI4Research 분야에서 혁신적 돌파구를 촉진하기를 기대합니다.
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex domains such as logical reasoning and experimental coding. Motivated by these advancements, numerous studies have explored the application of AI in the innovation process, particularly in the context of scientific research. These AI technologies primarily aim to develop systems that can autonomously conduct research processes across a wide range of scientific disciplines. Despite these significant strides, a comprehensive survey on AI for Research (AI4Research) remains absent, which hampers our understanding and impedes further development in this field. To address this gap, we present a comprehensive survey and offer a unified perspective on AI4Research. Specifically, the main contributions of our work are as follows: (1) Systematic taxonomy: We first introduce a systematic taxonomy to classify five mainstream tasks in AI4Research. (2) New frontiers: Then, we identify key research gaps and highlight promising future directions, focusing on the rigor and scalability of automated experiments, as well as the societal impact. (3) Abundant applications and resources: Finally, we compile a wealth of resources, including relevant multidisciplinary applications, data corpora, and tools. We hope our work will provide the research community with quick access to these resources and stimulate innovative breakthroughs in AI4Research.
논문 링크
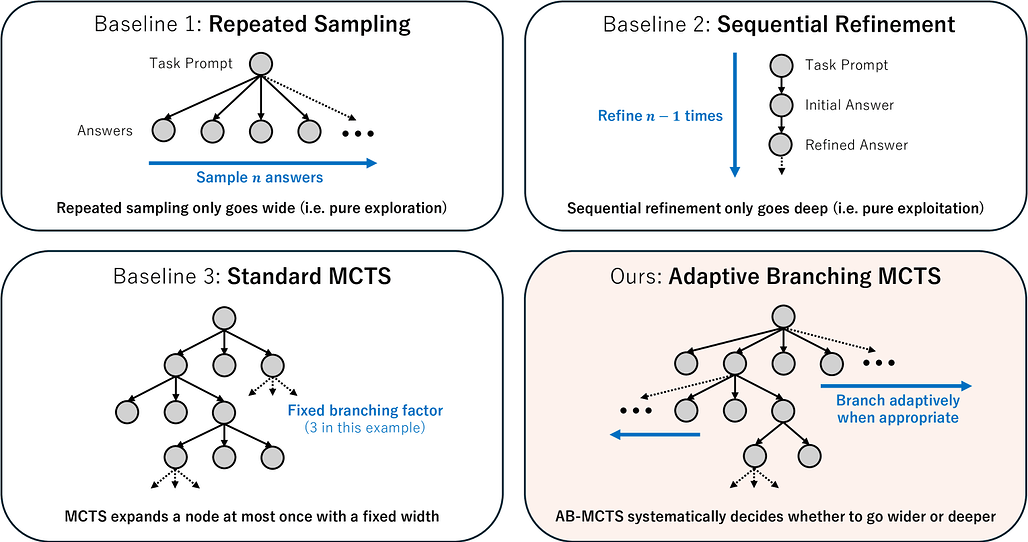
더 넓게 혹은 더 깊게? 적응형 분기 트리 탐색을 통한 LLM 추론 시 연산 확장 / Wider or Deeper? Scaling LLM Inference-Time Compute with Adaptive Branching Tree Search
논문 소개
최근 연구들은 추론 시 계산량 증가(Inference-time Computation)가 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 추론 능력 향상에 크게 기여함을 보여주었습니다. 본 연구에서는 외부 피드백 신호를 활용하여 반복 샘플링을 일반화한 적응형 분기 몬테카를로 트리 탐색(Adaptive Branching Monte Carlo Tree Search, AB-MCTS) 기법을 제안합니다. AB-MCTS는 탐색 트리의 각 노드에서 새로운 후보를 확장하는 ‘넓히기’와 기존 후보를 재탐색하는 ‘깊히기’를 동적으로 결정하여 다중 회차 탐색과 활용을 수행합니다. 복잡한 코딩 및 공학 문제에서 최첨단 모델을 활용한 실험 결과, AB-MCTS가 반복 샘플링과 기존 MCTS보다 우수한 성능을 보여, 응답 다양성과 다중 회차 해법 개선의 결합이 효과적인 추론 시간 확장에 중요함을 입증하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 연구들은 추론 시 계산량을 증가시키는 것이 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 추론 능력을 크게 향상시킬 수 있음을 보여주고 있습니다. 반복 샘플링(즉, 여러 후보 출력을 생성하는 것)은 매우 효과적인 전략이지만, 코딩과 같은 작업에서 흔히 활용 가능한 외부 피드백 신호를 활용하여 출력을 정제하지는 못합니다. 본 연구에서는 Adaptive Branching Monte Carlo Tree Search(AB-MCTS)라는 새로운 추론 시 프레임워크를 제안합니다. AB-MCTS는 원칙에 기반한 다회차 탐색과 활용을 통해 반복 샘플링을 일반화한 방법입니다. 탐색 트리의 각 노드에서 AB-MCTS는 외부 피드백 신호를 바탕으로 새로운 후보 응답을 확장하여 “더 넓게 가기” 또는 기존 응답을 재검토하여 “더 깊게 가기”를 동적으로 결정합니다. 최첨단 모델을 활용한 복잡한 코딩 및 엔지니어링 과제에서 본 방법을 평가한 결과, AB-MCTS는 반복 샘플링과 표준 MCTS 모두를 일관되게 능가함을 보여주었으며, LLM의 응답 다양성과 다회차 솔루션 정제의 결합이 효과적인 추론 시 확장에 있어 중요함을 강조합니다.
Recent advances demonstrate that increasing inference-time computation can significantly boost the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Although repeated sampling (i.e., generating multiple candidate outputs) is a highly effective strategy, it does not leverage external feedback signals for refinement, which are often available in tasks like coding. In this work, we propose Adaptive Branching Monte Carlo Tree Search (AB-MCTS), a novel inference-time framework that generalizes repeated sampling with principled multi-turn exploration and exploitation. At each node in the search tree, AB-MCTS dynamically decides whether to "go wider" by expanding new candidate responses or "go deeper" by revisiting existing ones based on external feedback signals. We evaluate our method on complex coding and engineering tasks using frontier models. Empirical results show that AB-MCTS consistently outperforms both repeated sampling and standard MCTS, underscoring the importance of combining the response diversity of LLMs with multi-turn solution refinement for effective inference-time scaling.
논문 링크
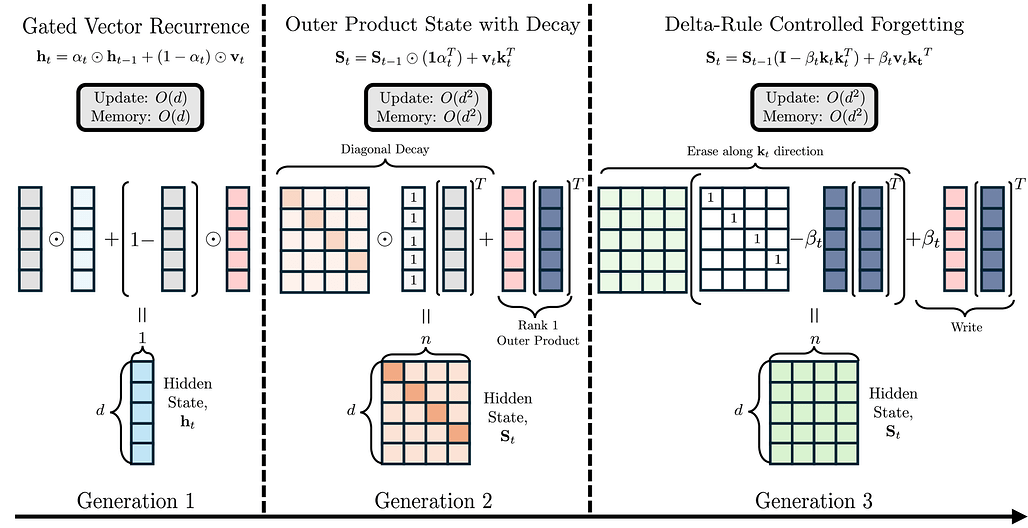
하이브리드 선형 어텐션의 체계적 분석 / A Systematic Analysis of Hybrid Linear Attention
논문 소개
트랜스포머는 긴 시퀀스 처리 시 계산량과 메모리 사용이 제곱적으로 증가하는 문제를 겪어, 고정 크기 은닉 상태를 활용하는 선형 어텐션(linear attention) 메커니즘이 도입되었습니다. 하지만 선형 어텐션은 기억 성능(recall)이 제한적이어서, 선형과 전체 어텐션(full attention)을 결합한 하이브리드 구조가 제안되었습니다. 본 연구에서는 다양한 선형 어텐션 모델을 독립적 및 하이브리드 형태로 체계적으로 평가하였으며, 특히 선택적 게이팅(selective gating), 계층적 순환(hierarchical recurrence), 그리고 제어된 망각(controlled forgetting)이 효과적인 하이브리드 모델 설계에 중요함을 밝혔습니다. 언어 모델링 성능은 선형과 전체 어텐션 비율에 크게 영향을 받지 않으나, 기억 성능은 전체 어텐션 비중이 3:1 이하일 때 크게 향상되며, HGRN-2 또는 GatedDeltaNet과 같은 아키텍처를 3:1~6:1 비율로 사용하는 것을 권장합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
트랜스포머는 긴 시퀀스 처리 시 이차 복잡도와 메모리 문제에 직면하여, 고정 크기 히든 상태를 사용하는 선형 어텐션 메커니즘이 도입되었습니다. 그러나 선형 모델은 종종 제한된 재현율 성능을 보이며, 이에 따라 선형과 전체 어텐션 레이어를 결합한 하이브리드 아키텍처가 제안되고 있습니다. 광범위한 하이브리드 아키텍처 연구에도 불구하고, 선형 어텐션 구성 요소의 선택에 대해서는 깊이 있는 탐구가 이루어지지 않았습니다. 본 연구에서는 벡터 순환부터 고급 게이팅 메커니즘에 이르는 다양한 세대의 선형 어텐션 모델을 독립형 및 하이브리드 형태로 체계적으로 평가하였습니다. 이를 위해 72개의 모델을 학습하고 오픈소스로 공개하였으며, 340M 파라미터(200억 토큰) 모델 36개와 1.3B 파라미터(1000억 토큰) 모델 36개로, 6가지 선형 어텐션 변형과 5가지 하이브리드 비율을 포함합니다. 표준 언어 모델링 및 재현율 벤치마크 결과, 우수한 독립형 선형 모델이 반드시 하이브리드에서 뛰어난 성능을 보이지는 않았습니다. 언어 모델링 성능은 선형-전체 어텐션 비율에 따라 안정적인 반면, 재현율은 전체 어텐션 레이어 비중이 증가할수록 특히 3:1 비율 이하에서 크게 향상되었습니다. 본 연구는 효과적인 하이브리드 모델을 위해 선택적 게이팅, 계층적 순환, 그리고 제어된 망각이 중요함을 강조합니다. Transformer 수준의 재현율을 효율적으로 달성하기 위해서는 선형-전체 어텐션 비율 3:1에서 6:1 사이의 HGRN-2 또는 GatedDeltaNet과 같은 아키텍처를 권장합니다. 본 연구에서 학습한 모델들은 Hybrid Linear Attention Research - a m-a-p Collection 에서 오픈소스로 제공됩니다.
Transformers face quadratic complexity and memory issues with long sequences, prompting the adoption of linear attention mechanisms using fixed-size hidden states. However, linear models often suffer from limited recall performance, leading to hybrid architectures that combine linear and full attention layers. Despite extensive hybrid architecture research, the choice of linear attention component has not been deeply explored. We systematically evaluate various linear attention models across generations - vector recurrences to advanced gating mechanisms - both standalone and hybridized. To enable this comprehensive analysis, we trained and open-sourced 72 models: 36 at 340M parameters (20B tokens) and 36 at 1.3B parameters (100B tokens), covering six linear attention variants across five hybridization ratios. Benchmarking on standard language modeling and recall tasks reveals that superior standalone linear models do not necessarily excel in hybrids. While language modeling remains stable across linear-to-full attention ratios, recall significantly improves with increased full attention layers, particularly below a 3:1 ratio. Our study highlights selective gating, hierarchical recurrence, and controlled forgetting as critical for effective hybrid models. We recommend architectures such as HGRN-2 or GatedDeltaNet with a linear-to-full ratio between 3:1 and 6:1 to achieve Transformer-level recall efficiently. Our models are open-sourced at Hybrid Linear Attention Research - a m-a-p Collection.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
![]() 파이토치 한국 사용자 모임
파이토치 한국 사용자 모임![]() 이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일
이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일![]() 로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
![]() 아래
아래![]() 쪽에 좋아요
쪽에 좋아요![]() 를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~
를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~ ![]()