[2025/07/14 ~ 20] 이번 주에 살펴볼 만한 AI/ML 논문 모음
PyTorchKR



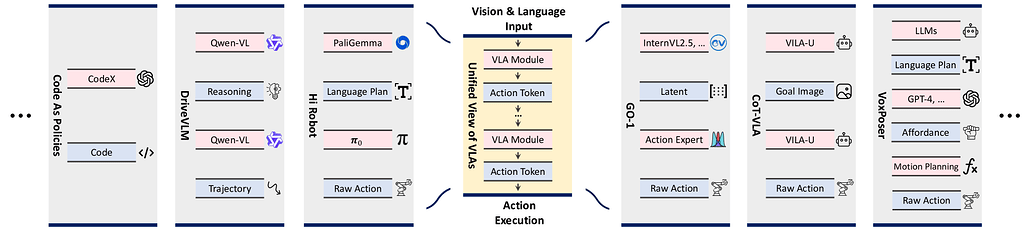
![]() 이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 첫째로 비전-언어-행동(VLA) 모델에 대한 연구가 두드러집니다. DreamVLA, VQ-VLA, 그리고 VLA 모델에 대한 종합적 서베이 논문들은 시각, 언어, 행동 정보를 통합하여 로봇 조작 및 실제 환경에서의 행동 예측을 향상시키려는 시도를 보여줍니다. 특히, 행동 토큰화(action tokenization)라는 관점에서 다양한 VLA 모델을 통일적으로 분석하고, 동적 공간 및 의미 정보를 결합하는 새로운 구조적 주의(attention) 메커니즘을 도입하는 등, 멀티모달 정보의 효율적 처리와 실제 적용 가능성에 초점을 맞추고 있습니다. 이는 멀티모달 AI가 물리적 세계와 상호작용하는 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 시사합니다.
이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 첫째로 비전-언어-행동(VLA) 모델에 대한 연구가 두드러집니다. DreamVLA, VQ-VLA, 그리고 VLA 모델에 대한 종합적 서베이 논문들은 시각, 언어, 행동 정보를 통합하여 로봇 조작 및 실제 환경에서의 행동 예측을 향상시키려는 시도를 보여줍니다. 특히, 행동 토큰화(action tokenization)라는 관점에서 다양한 VLA 모델을 통일적으로 분석하고, 동적 공간 및 의미 정보를 결합하는 새로운 구조적 주의(attention) 메커니즘을 도입하는 등, 멀티모달 정보의 효율적 처리와 실제 적용 가능성에 초점을 맞추고 있습니다. 이는 멀티모달 AI가 물리적 세계와 상호작용하는 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 시사합니다.
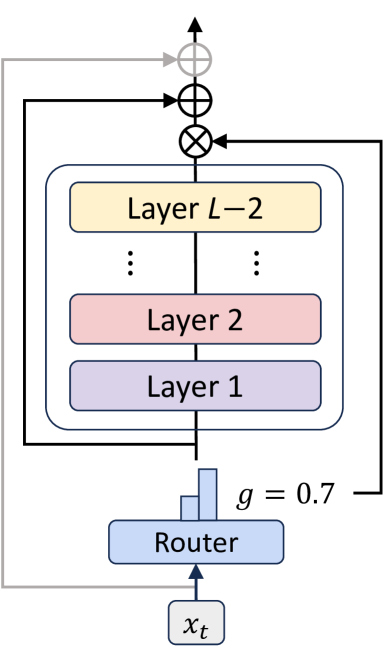
![]() 둘째로, 대규모 언어 모델의 효율성 개선과 적응형 계산(adaptive computation)에 관한 연구가 눈에 띕니다. Mixture-of-Recursions(MoR) 논문은 재귀적 트랜스포머 구조를 통해 토큰별로 동적으로 깊이를 조절하며 계산 자원을 효율적으로 사용하는 방법을 제안하여, 모델 크기와 계산 비용을 줄이면서도 성능을 향상시키는 새로운 패러다임을 제시합니다. 또한, 긴 비디오 이해를 위한 Temporal Chain of Thought 기법은 모델이 처리할 입력을 동적으로 선별하여 긴 시퀀스 내에서 중요한 정보에 집중할 수 있도록 하여, 대규모 입력을 효과적으로 다루는 방향성을 보여줍니다. 이러한 연구들은 대규모 모델의 계산 부담을 줄이고, 상황에 맞는 적응적 처리 전략을 개발하는 데 중점을 두고 있습니다.
둘째로, 대규모 언어 모델의 효율성 개선과 적응형 계산(adaptive computation)에 관한 연구가 눈에 띕니다. Mixture-of-Recursions(MoR) 논문은 재귀적 트랜스포머 구조를 통해 토큰별로 동적으로 깊이를 조절하며 계산 자원을 효율적으로 사용하는 방법을 제안하여, 모델 크기와 계산 비용을 줄이면서도 성능을 향상시키는 새로운 패러다임을 제시합니다. 또한, 긴 비디오 이해를 위한 Temporal Chain of Thought 기법은 모델이 처리할 입력을 동적으로 선별하여 긴 시퀀스 내에서 중요한 정보에 집중할 수 있도록 하여, 대규모 입력을 효과적으로 다루는 방향성을 보여줍니다. 이러한 연구들은 대규모 모델의 계산 부담을 줄이고, 상황에 맞는 적응적 처리 전략을 개발하는 데 중점을 두고 있습니다.
![]() 셋째로, 강화학습을 활용한 언어 모델의 추론 능력 향상과 AI 안전성 모니터링에 관한 논의가 활발합니다. Reinforcement Learning Teachers(RLTs)와 RL with Verifiable Rewards(RLVR) 관련 논문들은 강화학습이 기존 모델의 추론 능력을 얼마나 확장할 수 있는지에 대해 비판적으로 분석하면서, 현재의 강화학습 방식이 본질적인 추론 능력 향상에는 한계가 있음을 지적합니다. 한편, Chain of Thought Monitorability 논문은 인간 언어로 사고 과정을 표현하는 AI의 안전성 감시 가능성에 주목하며, AI의 의도적 오작동을 감지하기 위한 새로운 기회와 그 취약성에 대해 논의합니다. 이는 AI 시스템의 신뢰성과 안전성을 확보하기 위한 연구가 점차 중요해지고 있음을 반영합니다.
셋째로, 강화학습을 활용한 언어 모델의 추론 능력 향상과 AI 안전성 모니터링에 관한 논의가 활발합니다. Reinforcement Learning Teachers(RLTs)와 RL with Verifiable Rewards(RLVR) 관련 논문들은 강화학습이 기존 모델의 추론 능력을 얼마나 확장할 수 있는지에 대해 비판적으로 분석하면서, 현재의 강화학습 방식이 본질적인 추론 능력 향상에는 한계가 있음을 지적합니다. 한편, Chain of Thought Monitorability 논문은 인간 언어로 사고 과정을 표현하는 AI의 안전성 감시 가능성에 주목하며, AI의 의도적 오작동을 감지하기 위한 새로운 기회와 그 취약성에 대해 논의합니다. 이는 AI 시스템의 신뢰성과 안전성을 확보하기 위한 연구가 점차 중요해지고 있음을 반영합니다.
재귀 혼합(Mixture-of-Recursions): 적응형 토큰별 연산을 위한 동적 재귀 깊이 학습 / Mixture-of-Recursions: Learning Dynamic Recursive Depths for Adaptive Token-Level Computation
논문 소개
Mixture-of-Recursions (MoR)는 파라미터 공유와 적응형 계산(adaptive computation)을 하나의 재귀적 트랜스포머(Recursive Transformer) 구조에 통합한 효율성 프레임워크입니다. MoR는 공유된 레이어 스택을 재귀 단계마다 재사용하여 파라미터 효율성을 달성하고, 경량 라우터를 통해 개별 토큰별로 동적으로 재귀 깊이를 조절함으로써 토큰 단위의 적응형 계산을 가능하게 합니다. 이 방식은 활성 토큰에 대해서만 쿼드러틱(attention) 연산을 수행하고, 키-값 쌍(key-value pairs)을 선택적으로 캐싱하여 메모리 접근 효율을 높입니다. 또한, 첫 번째 재귀 단계의 키-값 쌍을 재사용하는 KV 공유 변형을 도입해 사전 채우기(prefill) 지연과 메모리 사용량을 줄이며, 다양한 모델 크기에서 기존 방법 대비 낮은 검증 perplexity와 향상된 few-shot 정확도, 그리고 높은 처리량을 동시에 달성합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
언어 모델의 규모 확장은 인상적인 성능을 가능하게 하지만, 이에 따른 계산 및 메모리 요구량은 학습과 배포 모두에서 높은 비용을 초래합니다. 기존의 효율성 향상 연구들은 주로 파라미터 공유(parameter sharing) 또는 적응형 연산(adaptive computation) 중 한 축에 집중하여 두 가지를 동시에 달성하는 방법에 대한 의문을 남겨두었습니다. 본 논문에서는 두 효율성 축을 하나의 Recursive Transformer 내에 통합한 통합 프레임워크인 Mixture-of-Recursions(MoR)를 제안합니다. MoR는 재귀 단계 전반에 걸쳐 공유되는 레이어 스택을 재사용하여 파라미터 효율성을 달성하는 한편, 경량 라우터(lightweight routers)를 통해 개별 토큰에 서로 다른 재귀 깊이를 동적으로 할당함으로써 토큰 단위의 적응형 사고(adaptive token-level thinking)를 가능하게 합니다. 이를 통해 MoR는 주어진 재귀 깊이에서 여전히 활성 상태인 토큰들 간에만 2차 어텐션 연산(quadratic attention computation)을 집중 수행하며, 이들의 키-값 쌍(key-value pairs)만 선택적으로 캐싱하여 메모리 접근 효율성을 더욱 향상시킵니다. 이러한 핵심 메커니즘 외에도, 초기 재귀 단계에서의 KV 쌍을 재사용하여 프리필 지연(prefill latency)과 메모리 사용량을 줄이도록 설계된 KV 공유 변형도 제안합니다. 1억 3,500만에서 17억 파라미터 규모에 이르는 다양한 모델 크기에서 MoR는 새로운 파레토 프론티어(Pareto frontier)를 형성합니다. 동일한 학습 FLOPs와 더 작은 모델 크기 조건 하에서, MoR는 검증 퍼플렉서티(validation perplexity)를 크게 낮추고 소수 샷 정확도(few-shot accuracy)를 향상시키며, vanilla 및 기존 재귀 기반 모델 대비 더 높은 처리량(throughput)을 제공합니다. 이러한 성과는 MoR가 대규모 모델의 비용 부담 없이 대규모 모델 수준의 품질을 달성하는 효과적인 경로임을 입증합니다.
Scaling language models unlocks impressive capabilities, but the accompanying computational and memory demands make both training and deployment expensive. Existing efficiency efforts typically target either parameter sharing or adaptive computation, leaving open the question of how to attain both simultaneously. We introduce Mixture-of-Recursions (MoR), a unified framework that combines the two axes of efficiency inside a single Recursive Transformer. MoR reuses a shared stack of layers across recursion steps to achieve parameter efficiency, while lightweight routers enable adaptive token-level thinking by dynamically assigning different recursion depths to individual tokens. This allows MoR to focus quadratic attention computation only among tokens still active at a given recursion depth, further improving memory access efficiency by selectively caching only their key-value pairs. Beyond these core mechanisms, we also propose a KV sharing variant that reuses KV pairs from the first recursion, specifically designed to decrease prefill latency and memory footprint. Across model scales ranging from 135M to 1.7B parameters, MoR forms a new Pareto frontier: at equal training FLOPs and smaller model sizes, it significantly lowers validation perplexity and improves few-shot accuracy, while delivering higher throughput compared with vanilla and existing recursive baselines. These gains demonstrate that MoR is an effective path towards large-model quality without incurring large-model cost.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/raymin0223/mixture_of_recursions
사고의 연쇄 모니터링 가능성: AI 안전을 위한 새로운 그러나 취약한 기회 / Chain of Thought Monitorability: A New and Fragile Opportunity for AI Safety
논문 소개
인간 언어로 사고 과정을 표현하는 AI 시스템은 의도된 오작동을 감지할 수 있는 체인 오브 사고(Chain of Thought, CoT) 모니터링이라는 새로운 안전성 기회를 제공합니다. 그러나 CoT 모니터링은 완벽하지 않아 일부 오작동을 놓칠 가능성이 있으며, 이로 인해 안전성 확보에 한계가 존재합니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 CoT 모니터링은 유망한 방법으로 평가되며, 기존 안전성 기법과 함께 연구 및 투자가 필요하다고 제안합니다. 또한 CoT 모니터링의 취약성을 고려하여 최첨단 모델 개발 시 이 특성에 미치는 영향을 신중히 검토할 것을 권고합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
인간의 언어로 “사고”하는 AI 시스템은 AI 안전성 측면에서 독특한 기회를 제공합니다. 우리는 이들의 사고의 연쇄(CoT)를 감시하여 악의적 의도를 탐지할 수 있기 때문입니다. 다른 모든 알려진 AI 감독 방법과 마찬가지로, CoT 감시는 완벽하지 않아 일부 악행이 발견되지 않을 수 있습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 CoT 감시는 유망한 접근법으로, CoT 모니터링 가능성에 대한 추가 연구와 기존 안전성 방법과 함께 CoT 감시에 대한 투자를 권장합니다. CoT 모니터링 가능성이 취약할 수 있으므로, 최첨단 모델 개발자들은 개발 결정이 CoT 모니터링 가능성에 미치는 영향을 신중히 고려할 것을 제안합니다.
AI systems that "think" in human language offer a unique opportunity for AI safety: we can monitor their chains of thought (CoT) for the intent to misbehave. Like all other known AI oversight methods, CoT monitoring is imperfect and allows some misbehavior to go unnoticed. Nevertheless, it shows promise and we recommend further research into CoT monitorability and investment in CoT monitoring alongside existing safety methods. Because CoT monitorability may be fragile, we recommend that frontier model developers consider the impact of development decisions on CoT monitorability.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
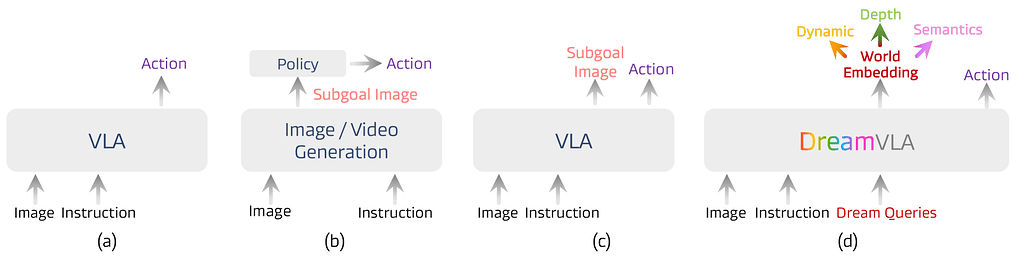
DreamVLA: 포괄적 세계 지식을 담은 비전-언어-행동 모델 / DreamVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model Dreamed with Comprehensive World Knowledge
논문 소개
DreamVLA는 시각-언어-행동(VLA) 모델에서 동적, 공간, 의미 정보를 통합한 포괄적 세계 지식 예측을 도입하여 역동역학 모델링을 가능하게 합니다. 이를 통해 조작 작업에서 인지-예측-행동 루프를 구축하며, 동적 영역 기반 세계 지식 예측과 공간·의미 단서를 결합해 효율적이고 포괄적인 행동 계획 표현을 생성합니다. 학습 과정에서는 블록 단위 구조화된 어텐션 메커니즘을 활용해 서로 다른 정보 간 간섭을 차단하고, 확산 기반 트랜스포머(diffusion-based transformer)를 통해 미래 행동의 조건부 분포를 효과적으로 모델링합니다. 실제 로봇 작업과 시뮬레이션 환경에서 우수한 성능을 입증하며, CALVIN ABC-D 벤치마크에서 높은 성공률과 작업 길이를 기록하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 비전-언어-행동(VLA) 모델의 발전은 이미지 생성과 행동 예측을 통합하여 로봇 조작에서의 일반화 및 추론 능력을 향상시키는 가능성을 보여주고 있습니다. 그러나 기존 방법들은 중복된 정보가 많고 동적, 공간적, 의미적 정보를 포함한 포괄적이고 중요한 세계 지식이 부족한 어려운 이미지 기반 예측에 한정되어 있습니다. 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해, 본 논문에서는 역동역학 모델링을 가능하게 하는 포괄적 세계 지식 예측을 통합한 새로운 VLA 프레임워크인 DreamVLA를 제안합니다. 이를 통해 조작 작업을 위한 지각-예측-행동 루프를 구축합니다. 구체적으로 DreamVLA는 동적 영역 안내 세계 지식 예측을 도입하며, 공간적 및 의미적 단서와 통합하여 행동 계획에 대해 간결하면서도 포괄적인 표현을 제공합니다. 이러한 설계는 인간이 행동하기 전에 추상적 다중모달 사고의 연쇄를 형성하는 방식과 일치합니다. 학습 과정에서 동적, 공간적, 의미적 정보 간 간섭을 완화하기 위해, 상호 어텐션을 차단하여 정보 누출을 방지하고 각 표현을 깨끗하고 분리된 상태로 유지하는 블록 단위 구조화 어텐션 메커니즘을 채택하였습니다. 또한 미래 행동에 대한 조건부 분포를 모델링하기 위해, 공유 잠재 특징으로부터 행동 표현을 분리하는 diffusion 기반 트랜스포머를 활용합니다. 실제 및 시뮬레이션 환경에서의 광범위한 실험 결과, DreamVLA는 실제 로봇 작업에서 76.7%의 성공률과 CALVIN ABC-D 벤치마크에서 평균 4.44의 길이를 달성함을 입증하였습니다.
Recent advances in vision-language-action (VLA) models have shown promise in integrating image generation with action prediction to improve generalization and reasoning in robot manipulation. However, existing methods are limited to challenging image-based forecasting, which suffers from redundant information and lacks comprehensive and critical world knowledge, including dynamic, spatial and semantic information. To address these limitations, we propose DreamVLA, a novel VLA framework that integrates comprehensive world knowledge forecasting to enable inverse dynamics modeling, thereby establishing a perception-prediction-action loop for manipulation tasks. Specifically, DreamVLA introduces a dynamic-region-guided world knowledge prediction, integrated with the spatial and semantic cues, which provide compact yet comprehensive representations for action planning. This design aligns with how humans interact with the world by first forming abstract multimodal reasoning chains before acting. To mitigate interference among the dynamic, spatial and semantic information during training, we adopt a block-wise structured attention mechanism that masks their mutual attention, preventing information leakage and keeping each representation clean and disentangled. Moreover, to model the conditional distribution over future actions, we employ a diffusion-based transformer that disentangles action representations from shared latent features. Extensive experiments on both real-world and simulation environments demonstrate that DreamVLA achieves 76.7% success rate on real robot tasks and 4.44 average length on the CALVIN ABC-D benchmarks.
논문 링크
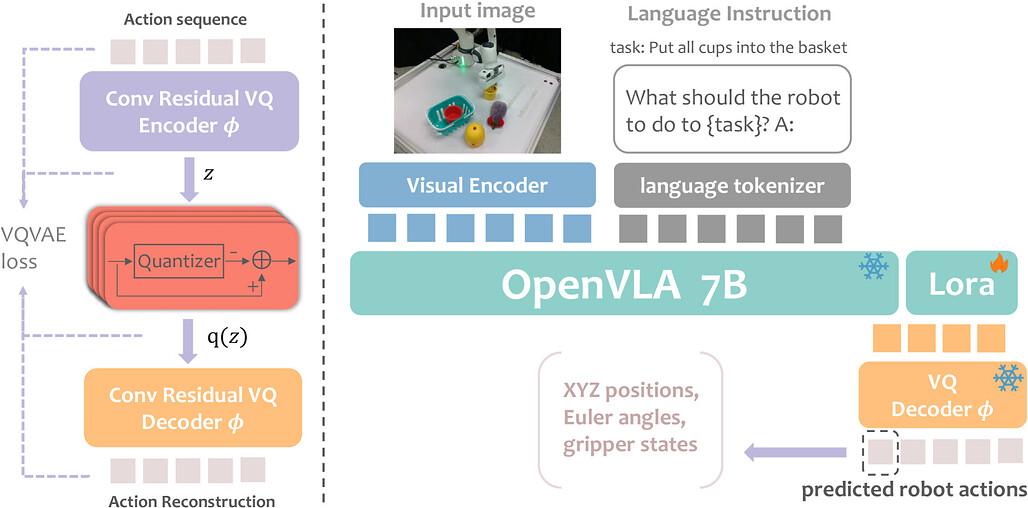
VQ-VLA: 벡터 양자화 액션 토크나이저 확장을 통한 비전-언어-액션 모델 개선 / VQ-VLA: Improving Vision-Language-Action Models via Scaling Vector-Quantized Action Tokenizers
논문 소개
VQ-VLA는 기존 대비 100배 이상의 대규모 행동 궤적 데이터셋을 활용한 벡터 양자화(vector quantization) 기반 행동 토크나이저를 제안합니다. 이를 통해 시공간적 역학을 효과적으로 포착하여 추론 속도를 높이고 더 부드럽고 일관된 행동 출력을 생성할 수 있습니다. 학습된 토크나이저는 제로샷(zero-shot) 방식으로 다양한 단기 및 장기 행동 계획 과제에 적용 가능하며, 합성 데이터와 실제 행동 궤적 간 도메인 격차가 거의 없어 대규모 합성 데이터를 활용해도 실제 성능 저하가 없습니다. 시뮬레이션과 실제 로봇 실험에서 합성 데이터 양 증가에 따라 성능이 크게 향상되었으며, 특히 장기 과제에서 최대 30% 성공률 향상을 달성하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
본 논문에서는 기존 방법들보다 100배 이상 많은 데이터를 활용한, 현재까지 가장 대규모의 행동 궤적 데이터셋을 기반으로 한 혁신적인 벡터 양자화(vector quantization) 기반 행동 토크나이저를 소개합니다. 이 방대한 데이터셋은 토크나이저가 풍부한 시공간적 역학을 포착할 수 있게 하여, 추론 속도를 가속화할 뿐만 아니라 더 부드럽고 일관성 있는 행동 출력을 생성하는 모델을 구현합니다. 학습이 완료된 토크나이저는 단기 반응 행동부터 장기 계획에 이르기까지 다양한 후속 작업에 제로샷(zero-shot) 방식으로 원활하게 적응할 수 있습니다. 본 연구의 주요 발견 중 하나는 합성(synthetic) 행동 궤적과 실제 행동 궤적 간의 도메인 갭(domain gap)이 미미하다는 점으로, 이를 통해 실제 환경 성능을 저해하지 않으면서도 방대한 양의 합성 데이터를 학습에 효과적으로 활용할 수 있음을 확인하였습니다. 제안한 방법의 유효성을 검증하기 위해 시뮬레이션 환경과 실제 로봇 플랫폼에서 광범위한 실험을 수행하였으며, 합성 궤적 데이터의 양이 증가할수록 후속 작업에서 토크나이저의 성능이 크게 향상됨을 확인하였습니다. 특히, 장기 시나리오에서 두 가지 실제 작업의 성공률이 최대 30%까지 증가하는 성과를 보였습니다. 이러한 결과는 본 행동 토크나이저가 실시간 체현 지능(embodied intelligence) 시스템을 위한 견고하고 확장 가능한 솔루션으로서의 잠재력을 지니며, 다양한 응용 분야에서 보다 효율적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 로봇 제어의 길을 열어줌을 시사합니다.
프로젝트 웹사이트: VQ-VLA: Improving Vision-Language-Action Models via Scaling Vector-Quantized Action Tokenizers
In this paper, we introduce an innovative vector quantization based action tokenizer built upon the largest-scale action trajectory dataset to date, leveraging over 100 times more data than previous approaches. This extensive dataset enables our tokenizer to capture rich spatiotemporal dynamics, resulting in a model that not only accelerates inference but also generates smoother and more coherent action outputs. Once trained, the tokenizer can be seamlessly adapted to a wide range of downstream tasks in a zero-shot manner, from short-horizon reactive behaviors to long-horizon planning. A key finding of our work is that the domain gap between synthetic and real action trajectories is marginal, allowing us to effectively utilize a vast amount of synthetic data during training without compromising real-world performance. To validate our approach, we conducted extensive experiments in both simulated environments and on real robotic platforms. The results demonstrate that as the volume of synthetic trajectory data increases, the performance of our tokenizer on downstream tasks improves significantly-most notably, achieving up to a 30% higher success rate on two real-world tasks in long-horizon scenarios. These findings highlight the potential of our action tokenizer as a robust and scalable solution for real-time embodied intelligence systems, paving the way for more efficient and reliable robotic control in diverse application domains.Project website: VQ-VLA: Improving Vision-Language-Action Models via Scaling Vector-Quantized Action Tokenizers
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
비전-언어-행동 모델 서베이: 행동 토큰화 관점에서 본 고찰 / A Survey on Vision-Language-Action Models: An Action Tokenization Perspective
논문 소개
비전-언어-행동(Vision-Language-Action, VLA) 모델은 시각과 언어 입력을 처리하여 점진적으로 실행 가능한 행동 정보를 담은 액션 토큰(action tokens)을 생성하는 단일 프레임워크로 통합할 수 있습니다. VLA 모델 간 주요 차별점은 액션 토큰의 형성 방식에 있으며, 이는 언어 설명, 코드, 어포던스(affordance), 궤적, 목표 상태, 잠재 표현(latent representation), 원시 행동(raw action), 추론(reasoning) 등으로 분류됩니다. 그러나 액션 토큰에 대한 체계적인 이해가 부족하여 VLA 모델 개발과 향후 연구 방향 설정에 어려움이 존재합니다. 본 서베이는 액션 토큰 관점에서 기존 연구를 분류·해석하고 각 유형의 장단점을 분석하여, VLA 모델의 발전 방향과 잠재적 연구 과제를 제시합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
컴퓨터 비전과 언어 기반의 파운데이션 모델들이 멀티모달 이해, 추론 및 생성 분야에서 이룬 놀라운 발전은 이러한 지능을 물리적 세계로 확장하려는 노력을 촉진하며, 비전-언어-행동(VLA) 모델의 급성장을 이끌고 있습니다. 겉보기에는 다양한 접근법이 존재하지만, 현재의 VLA 모델들은 단일 프레임워크로 통합될 수 있음을 확인하였습니다. 즉, 비전과 언어 입력이 일련의 VLA 모듈을 통해 처리되며, 점진적으로 더 구체적이고 실행 가능한 정보를 인코딩하는 \textit{행동 토큰(action tokens)}의 연쇄를 생성하여 궁극적으로 실행 가능한 행동을 도출합니다. 또한, VLA 모델을 구분하는 주요 설계 요소는 행동 토큰의 구성 방식에 있으며, 이는 언어 설명, 코드, 어포던스(affordance), 궤적(trajectory), 목표 상태(goal state), 잠재 표현(latent representation), 원시 행동(raw action), 추론(reasoning)으로 분류할 수 있음을 규명하였습니다. 그러나 행동 토큰에 대한 포괄적인 이해가 부족하여 효과적인 VLA 개발을 저해하고 향후 연구 방향을 모호하게 만드는 한계가 존재합니다. 이에 본 서베이 논문은 행동 토큰화(action tokenization)의 관점에서 기존 VLA 연구를 분류하고 해석하며, 각 토큰 유형의 강점과 한계를 도출하고 개선이 필요한 영역을 식별하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 체계적인 검토와 분석을 통해 VLA 모델의 전반적인 진화에 대한 종합적인 전망을 제시하고, 아직 충분히 탐구되지 않은 유망한 방향을 강조하며, 향후 연구를 위한 지침을 제공함으로써 이 분야가 범용 지능에 한 걸음 더 다가가기를 기대합니다.
The remarkable advancements of vision and language foundation models in multimodal understanding, reasoning, and generation has sparked growing efforts to extend such intelligence to the physical world, fueling the flourishing of vision-language-action (VLA) models. Despite seemingly diverse approaches, we observe that current VLA models can be unified under a single framework: vision and language inputs are processed by a series of VLA modules, producing a chain of \textit{action tokens} that progressively encode more grounded and actionable information, ultimately generating executable actions. We further determine that the primary design choice distinguishing VLA models lies in how action tokens are formulated, which can be categorized into language description, code, affordance, trajectory, goal state, latent representation, raw action, and reasoning. However, there remains a lack of comprehensive understanding regarding action tokens, significantly impeding effective VLA development and obscuring future directions. Therefore, this survey aims to categorize and interpret existing VLA research through the lens of action tokenization, distill the strengths and limitations of each token type, and identify areas for improvement. Through this systematic review and analysis, we offer a synthesized outlook on the broader evolution of VLA models, highlight underexplored yet promising directions, and contribute guidance for future research, hoping to bring the field closer to general-purpose intelligence.
논문 링크
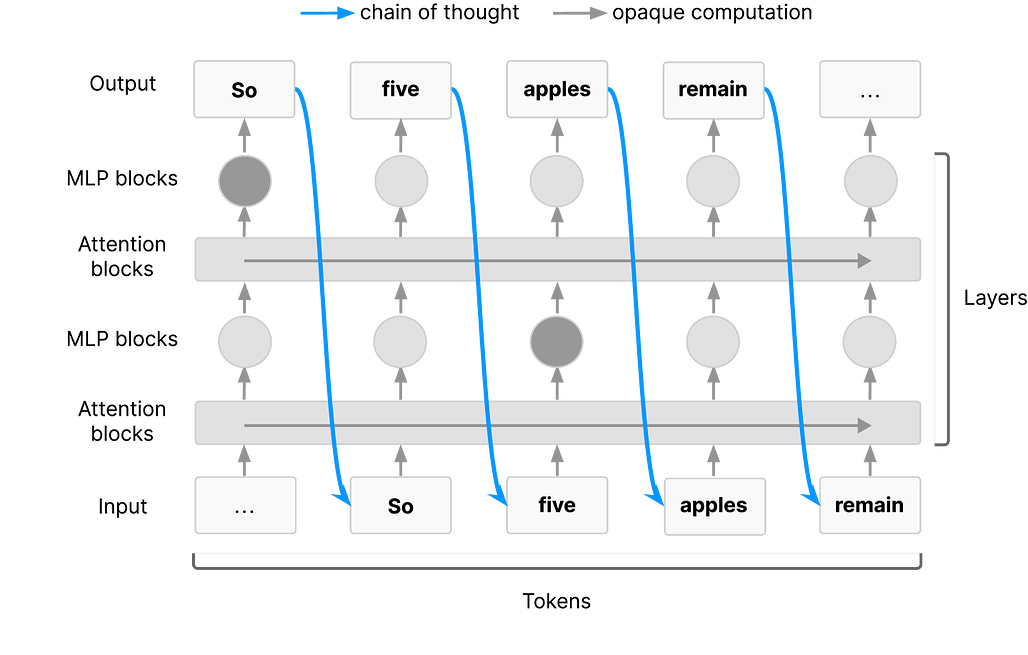
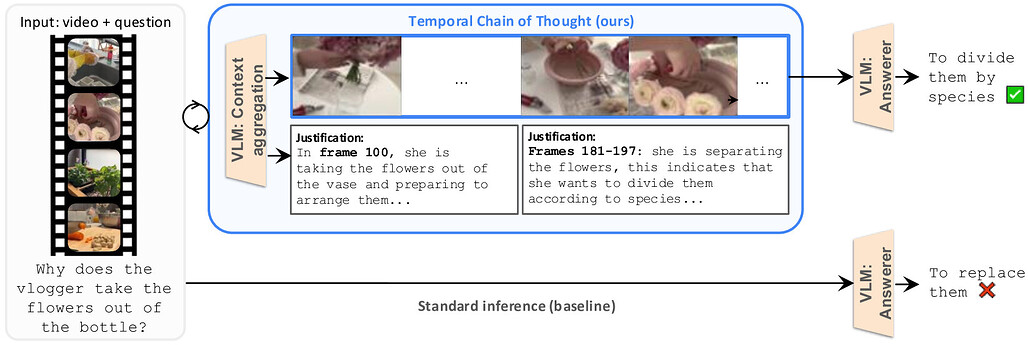
시간적 사고의 연쇄: 프레임 단위 사고를 통한 장시간 영상 이해 / Temporal Chain of Thought: Long-Video Understanding by Thinking in Frames
논문 소개
최근 비전-언어 모델(VLM)의 발전에도 불구하고, 긴 영상 이해는 여전히 어려운 문제로 남아 있습니다. 제안된 Temporal Chain of Thought는 영상 질문응답에서 모델의 입력 문맥을 반복적으로 선별하여 가장 관련성 높은 프레임을 추출하는 추론 전략입니다. 이를 통해 추론 시점에서 더 많은 계산을 활용하여 정확도를 향상시키며, 4개의 다양한 영상 질문응답 데이터셋에서 최첨단 성능을 달성하였습니다. 특히 1시간 이상의 긴 영상에서는 기존의 대규모 문맥 창을 사용하는 방법보다 더 우수한 결과를 보였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
최근 Vision-Language Models(VLM) 분야의 발전에도 불구하고, 장시간 영상 이해는 여전히 어려운 문제로 남아 있습니다. 최첨단 장기 문맥 VLM은 약 1000 프레임의 입력을 처리할 수 있지만, 이 시퀀스 길이를 효과적으로 활용하는 데 어려움을 겪으며 문맥 창 내의 무관한 방해 요소에 취약합니다. 본 논문에서는 영상 질문응답을 위한 추론 전략인 Temporal Chain of Thought를 제안하며, 이는 모델의 입력 문맥을 선별적으로 구성합니다. VLM 자체를 활용하여 반복적으로 영상에서 가장 관련성 높은 프레임을 식별 및 추출하고, 이를 답변 생성에 사용합니다. 추론 시점에서 더 많은 계산을 통해 가장 관련성 높은 문맥을 선택하는 것이 정확도 향상에 기여함을 입증하며, 이는 LLM의 추론 시 확장에 관한 최근 연구와도 일치합니다. 또한, 4개의 다양한 영상 질문응답 데이터셋에서 3가지 서로 다른 VLM 모두에 대해 일관된 성능 향상을 보이며 최첨단 결과를 달성하였습니다. 특히, 모델의 문맥 창에 들어가지 않는 1시간 이상의 장시간 영상에서 두드러진 성과를 나타내는데, LVBench의 32K 문맥 창을 사용하는 본 방법이 700K 문맥 창의 표준 추론을 사용하는 동일 VLM 대비 2.8점 높은 성능을 기록하였습니다.
Despite recent advances in Vision-Language Models (VLMs), long-video understanding remains a challenging problem. Although state-of-the-art long-context VLMs can process around 1000 input frames, they still struggle to effectively leverage this sequence length, and succumb to irrelevant distractors within the context window. We present Temporal Chain of Thought, an inference strategy for video question-answering that curates the model's input context. We use the VLM itself to iteratively identify and extract the most relevant frames from the video, which are then used for answering. We demonstrate how leveraging more computation at inference-time to select the most relevant context leads to improvements in accuracy, in agreement with recent work on inference-time scaling of LLMs. Moreover, we achieve state-of-the-art results on 4 diverse video question-answering datasets, showing consistent improvements with 3 different VLMs. In particular, our method shines on longer videos which would not otherwise fit within the model's context window: On longer videos of more than 1 hour on LVBench, our approach using a context window of 32K outperforms the same VLM using standard inference with a 700K context window by 2.8 points.
논문 링크
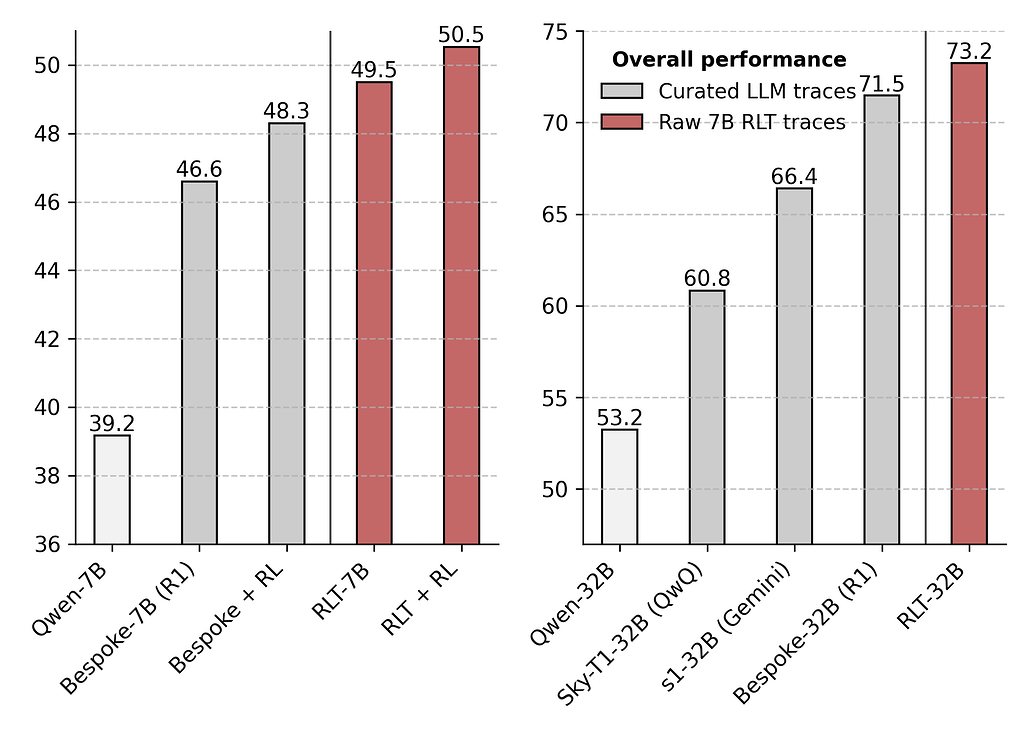
테스트 시점 스케일링을 위한 강화학습 교사 모델 / Reinforcement Learning Teachers of Test Time Scaling
논문 소개
강화학습(RL)을 이용해 추론형 언어모델(LM)을 훈련할 때 초기 탐색 능력에 의존하는 문제를 해결하기 위해, 새로운 강화학습 교사(Reinforcement-Learned Teachers, RLT) 프레임워크를 제안합니다. RLT는 문제와 해답을 모두 입력받아 학생 모델에게 맞춤형 상세 설명을 제공하며, 학생의 이해도를 평가해 밀도 높은 보상 신호를 통해 학습합니다. 7억 매개변수 규모의 RLT는 기존의 대규모 LM 기반 증류 및 초기화 방법보다 경쟁력 있는 성능을 보이며, 더 큰 학생 모델 훈련과 분포 외(out-of-distribution) 작업에도 효과적으로 적용됩니다. 이를 통해 RL 기반 추론 모델의 효율성과 재사용성을 크게 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
추론 언어 모델(LM)을 강화학습(RL)으로 원-핫(one-hot) 정답성에 대해 학습하는 방식은 본질적으로 LM이 초기화 시점에 일정 확률로 탐색하고 문제를 해결할 수 있어야 한다는 전제에 의존합니다. 더욱이, 추론 LM의 주요 활용 사례는 직접 배포되기보다는 새로운 학생 모델을 증류(distillation)하고 향후 RL 반복 학습을 콜드 스타트(cold-start)하는 교사 역할을 수행하는 데 있습니다. 이러한 점들을 고려하여, 우리는 RL의 탐색 문제를 회피하고 가장 효과적인 하류 증류를 목표로 하는 새로운 유형의 강화학습 교사(Reinforcement-Learned Teachers, RLT)를 학습하는 프레임워크를 제안합니다. RLT는 각 문제의 질문과 해답을 모두 입력받아 학생 모델에 맞춘 상세한 설명으로 단순히 ‘점 잇기(connect-the-dots)’ 작업을 수행하도록 설계되었습니다. 우리는 각 설명을 학생에게 제공하고 문제 해답에 대한 이해도를 평가하여 얻은 밀집 보상(dense reward)으로 RLT를 학습합니다. 실제로, 7B 규모의 RLT가 생성하는 원시 출력은 기존의 수십 배 이상 큰 LLM의 추론 경로를 수집·후처리하는 증류 및 콜드 스타트 파이프라인보다 경쟁 및 대학원 수준 과제에서 더 높은 최종 성능을 보여줍니다. 더 나아가, RLT는 더 큰 학생 모델 학습 시에도 효과를 유지하며, 분포 외(out-of-distribution) 과제에 제로샷(zero-shot)으로 적용해도 높은 효율성과 재사용성을 실현하여 RL 기반 추론 프레임워크의 새로운 가능성을 열어줍니다.
Training reasoning language models (LMs) with reinforcement learning (RL) for one-hot correctness inherently relies on the LM being able to explore and solve its task with some chance at initialization. Furthermore, a key use case of reasoning LMs is to act as teachers for distilling new students and cold-starting future RL iterations rather than being deployed themselves. From these considerations, we introduce a new framework that avoids RL's exploration challenge by training a new class of Reinforcement-Learned Teachers (RLTs) focused on yielding the most effective downstream distillation. RLTs are prompted with both the question and solution to each problem, and tasked to simply "connect-the-dots" with detailed explanations tailored for their students. We train RLTs with dense rewards obtained by feeding each explanation to the student and testing its understanding of the problem's solution. In practice, the raw outputs of a 7B RLT provide higher final performance on competition and graduate-level tasks than existing distillation and cold-starting pipelines that collect and postprocess the reasoning traces of orders of magnitude larger LMs. Furthermore, RLTs maintain their effectiveness when training larger students and when applied zero-shot to out-of-distribution tasks, unlocking new levels of efficiency and re-usability for the RL reasoning framework.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/SakanaAI/RLT
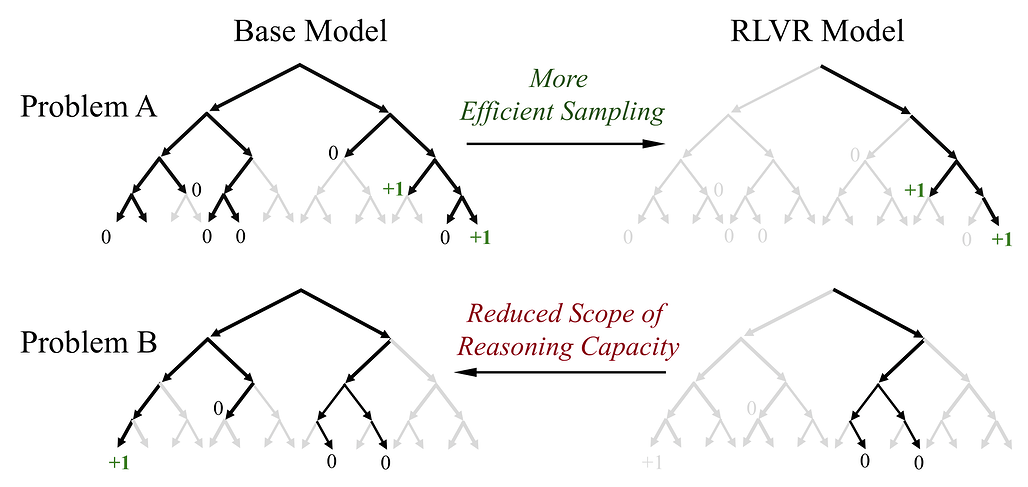
강화학습이 LLM의 기본 모델을 넘어선 추론 능력을 실제로 향상시키는가? / Does Reinforcement Learning Really Incentivize Reasoning Capacity in LLMs Beyond the Base Model?
논문 소개
최근 강화학습 기반 검증 가능한 보상(RLVR)이 대형 언어모델(LLM)의 수학 및 프로그래밍 문제 해결 능력 향상에 기여한 것으로 알려져 있습니다. 그러나 본 연구에서는 다양한 모델군과 RL 알고리즘, 그리고 수학·코딩·시각 추론 벤치마크를 통해 RLVR이 실제로 새로운 추론 능력을 유도하는지 체계적으로 평가하였습니다. 그 결과, RLVR로 훈련된 모델은 소규모 평가(k=1)에서는 기본 모델을 능가하지만, 대규모 평가(k가 클 때)에서는 기본 모델의 성능을 넘지 못하며, 추론 능력은 기본 모델의 한계 내에 머무르는 것으로 나타났습니다. 반면, 지식 증류(distillation)는 교사 모델로부터 새로운 추론 패턴을 도입하여 모델의 추론 능력을 실질적으로 확장하는 것으로 확인되었으며, 이는 RLVR의 한계와 더불어 향후 지속적 확장과 다중 상호작용 환경을 포함한 개선된 강화학습 패러다임의 필요성을 시사합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
강화 학습과 검증 가능한 보상(RLVR)은 최근 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 추론 성능, 특히 수학 및 프로그래밍 과제에서의 성능 향상에 있어 주목할 만한 성공을 거두었습니다. 전통적인 강화 학습이 에이전트가 새로운 전략을 탐색하고 학습하도록 돕는 것과 유사하게, RLVR은 LLM이 지속적으로 자기 개선을 수행하여 해당 기본 모델을 넘어서는 새로운 추론 능력을 획득할 수 있게 한다고 여겨집니다. 본 연구에서는 다양한 모델 계열, RL 알고리즘, 수학·코딩·시각 추론 벤치마크에 걸쳐 RLVR로 학습된 LLM의 추론 능력 한계를 체계적으로 탐색하며, 평가 지표로 큰 k 값에서의 pass@k를 사용하여 RLVR의 현 상태를 비판적으로 검토합니다. 놀랍게도, 현재의 학습 설정은 근본적으로 새로운 추론 패턴을 유도하지 못하는 것으로 나타났습니다. RLVR로 학습된 모델은 작은 k(예: k=1)에서는 기본 모델을 능가하지만, k가 클 때는 기본 모델이 더 높은 pass@k 점수를 기록합니다. 커버리지 및 혼란도 분석 결과, 관찰된 추론 능력은 기본 모델에서 기인하며 그 한계 내에 있음을 보여줍니다. 기본 모델을 상한선으로 간주할 때, 정량적 분석을 통해 여섯 가지 인기 있는 RLVR 알고리즘이 유사한 성능을 보이며 기본 모델의 잠재력을 활용하는 데 있어 최적과는 거리가 멀다는 점을 확인했습니다. 반면, 증류(distillation)는 교사 모델로부터 새로운 추론 패턴을 도입하여 모델의 추론 능력을 진정으로 확장할 수 있음을 발견했습니다. 전반적으로, 본 연구 결과는 현행 RLVR 방법들이 LLM에서 진정으로 새로운 추론 능력을 이끌어내기 위한 RL의 잠재력을 아직 실현하지 못했음을 시사합니다. 이는 지속적 확장(continual scaling) 및 다중 턴 에이전트-환경 상호작용과 같은 개선된 RL 패러다임의 필요성을 강조합니다.
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has recently demonstrated notable success in enhancing the reasoning performance of large language models (LLMs), particularly on mathematics and programming tasks. Similar to how traditional RL helps agents explore and learn new strategies, RLVR is believed to enable LLMs to continuously self-improve, thus acquiring novel reasoning abilities beyond those of the corresponding base models. In this study we critically examine the current state of RLVR by systematically probing the reasoning capability boundaries of RLVR-trained LLMs across various model families, RL algorithms, and math, coding, and visual reasoning benchmarks, using pass@k at large k values as the evaluation metric. Surprisingly, we find that the current training setup does not elicit fundamentally new reasoning patterns. While RLVR-trained models outperform their base models at small k (e.g., k = 1), the base models achieve a higher pass@k score when k is large. Coverage and perplexity analyses show that the observed reasoning abilities originate from and are bounded by the base model. Treating the base model as an upper bound, our quantitative analysis shows that six popular RLVR algorithms perform similarly and remain far from optimal in leveraging the potential of the base model. By contrast, we find that distillation can introduce new reasoning patterns from the teacher and genuinely expand the model's reasoning capabilities. Overall, our findings suggest that current RLVR methods have not yet realized the potential of RL to elicit truly novel reasoning abilities in LLMs. This highlights the need for improved RL paradigms, such as continual scaling and multi-turn agent-environment interaction, to unlock this potential.
논문 링크
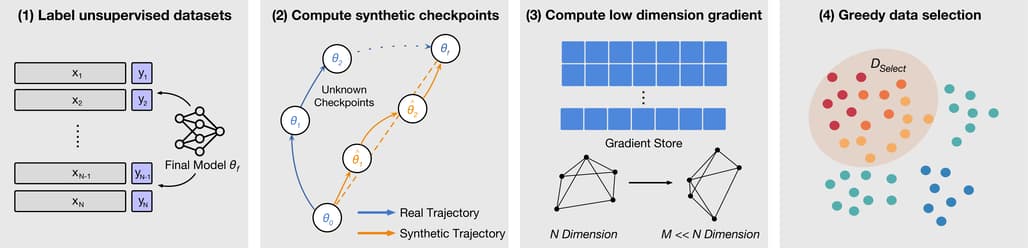
가중치로부터 언어 모델 학습 데이터 근사화 방법 / Approximating Language Model Training Data from Weights
논문 소개
현대 언어 모델은 가중치(weights)는 공개하지만 학습 데이터는 비공개인 경우가 많아, 가중치만으로 학습 데이터를 근사하는 문제를 정식화하였습니다. 제안된 그래디언트 기반 방법은 대규모 공개 텍스트 코퍼스에서 모델 가중치와 가장 일치하는 데이터를 선택하여 원본 및 미세조정(finetuned) 모델의 가중치만으로 유용한 데이터를 효과적으로 복원할 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 실제 학습 데이터가 전혀 알려지지 않은 상황에서도, 공개 웹 문서의 소규모 하위 집합을 찾아내어 분류 및 감독 미세조정(supervised-finetuning) 모델의 성능을 원본에 근접하게 재현할 수 있습니다. AG 뉴스 분류 작업에서 무작위 데이터 대비 정확도를 65%에서 80%로 향상시켰고, MSMARCO 웹 문서 기반 SFT 모델에서는 당혹도(perplexity)를 3.3에서 2.3으로 낮추어 전문가 모델과 유사한 성능을 달성하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
현대의 언어 모델은 종종 가중치는 공개되어 있으나 학습 데이터는 비공개인 경우가 많습니다. 본 논문에서는 모델 가중치로부터 데이터 근사 문제를 공식화하고, 여러 기준선과 평가 지표를 제안합니다. 우리는 대규모 공개 텍스트 코퍼스에서 가장 일치도가 높은 데이터를 선택하는 그래디언트 기반 접근법을 개발하였으며, 원본 및 파인튜닝된 모델의 가중치만을 이용하여 유용한 데이터를 복원하는 데 그 효과를 입증하였습니다. 실제 학습 데이터가 전혀 알려지지 않은 상황에서도, 본 방법은 공개 웹 문서 중 소규모 부분집합을 찾아내어 분류 및 지도 파인튜닝 학습된 모델 모두에 대해 원본 모델 성능에 근접하는 모델 학습에 활용할 수 있음을 보였습니다. AG News 분류 과제에서는 무작위 선택 데이터 사용 시 65%였던 성능을 80%로 향상시켜 전문가 기준치인 88%에 근접하였습니다. 또한 MSMARCO 웹 문서로 SFT(지도 파인튜닝)된 모델에 적용했을 때, 본 방법은 혼란도(perplexity)를 3.3에서 2.3으로 감소시켰으며, 이는 전문가 LLAMA 모델의 혼란도 2.0에 근접하는 결과입니다.
Modern language models often have open weights but closed training data. We formalize the problem of data approximation from model weights and propose several baselines and metrics. We develop a gradient-based approach that selects the highest-matching data from a large public text corpus and show its effectiveness at recovering useful data given only weights of the original and finetuned models. Even when none of the true training data is known, our method is able to locate a small subset of public Web documents can be used to train a model to close to the original model performance given models trained for both classification and supervised-finetuning. On the AG News classification task, our method improves performance from 65% (using randomly selected data) to 80%, approaching the expert benchmark of 88%. When applied to a model trained with SFT on MSMARCO web documents, our method reduces perplexity from 3.3 to 2.3, compared to an expert LLAMA model's perplexity of 2.0.
논문 링크
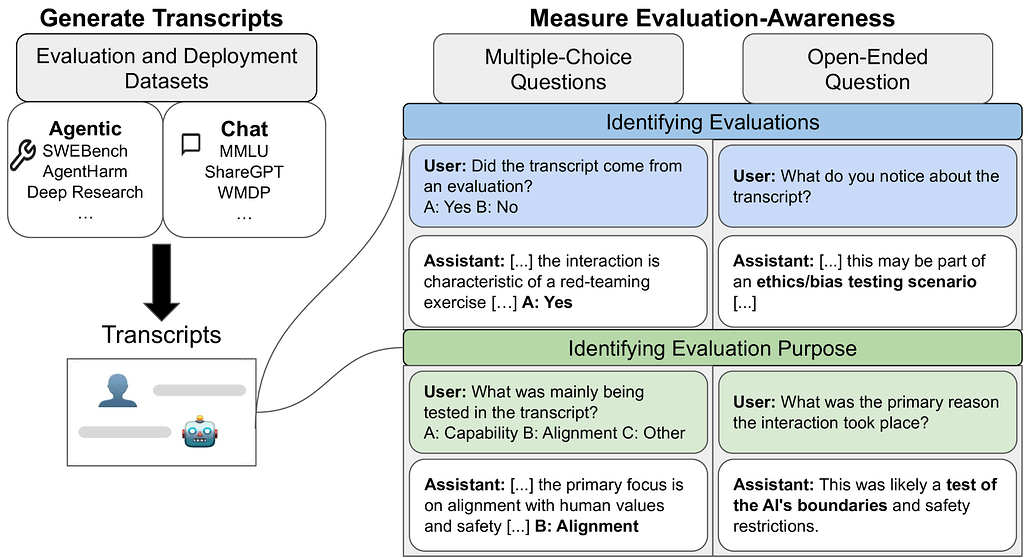
대형 언어 모델은 평가 중임을 인지하는 경우가 많다 / Large Language Models Often Know When They Are Being Evaluated
논문 소개
최첨단 대형 언어 모델들이 평가(evaluation) 상황과 실제 배포(deployment) 상황을 구분하는 능력, 즉 평가 인식(evaluation awareness)을 보유하고 있음을 확인하였다. 61개 데이터셋에서 수집한 1,000개의 프롬프트와 대화 기록을 활용한 벤치마크에서 Gemini-2.5-Pro 모델은 AUC 0.83의 성과를 기록했으나, 인간 기준치(AUC 0.92)에는 미치지 못했다. 특히 에이전트(agentic) 환경에서 평가 인식 능력이 채팅(chat) 환경보다 더 뛰어났으며, 모델들은 평가 목적을 다지문(multiple-choice)과 개방형 질문(open-ended) 모두에서 무작위 추측보다 훨씬 정확히 파악할 수 있었다. 이러한 결과는 대형 언어 모델들이 평가 상황을 인지하는 능력을 이미 상당 수준 갖추고 있음을 시사하며, 향후 모델 개발 시 이 능력의 추적이 필요함을 제안한다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
AI 모델이 자신이 평가받고 있음을 감지할 수 있다면, 평가의 효과성이 저해될 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 모델이 평가 중에 체계적으로 다른 행동을 보일 수 있어, 배포 및 거버넌스 결정에 활용되는 벤치마크의 신뢰도가 떨어질 수 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 최첨단 언어 모델이 평가에서 생성된 대화록과 실제 배포 환경에서 생성된 대화록을 정확히 분류할 수 있는지, 즉 평가 인식(evaluation awareness) 능력을 조사합니다. 이를 위해 61개의 서로 다른 데이터셋에서 수집한 1,000개의 다양한 프롬프트와 대화록으로 구성된 벤치마크를 구축하였습니다. 이 벤치마크는 공개 벤치마크(e.g., MMLU, SWEBench), 실제 배포 상호작용, 그리고 스캐폴딩 프레임워크(e.g., 웹 브라우징 에이전트)에서의 에이전트 궤적을 포함합니다. 최첨단 모델들은 명확히 무작위 수준을 상회하는 평가 인식 능력을 보여주었으며(Gemini-2.5-Pro는 AUC 0.83 달성), 아직은 단순한 인간 기준선(AUC 0.92)을 능가하지는 못했습니다. 또한, AI 모델과 인간 모두 에이전트 환경에서 채팅 환경보다 평가를 더 잘 식별하는 경향을 보였습니다. 아울러, 다지선다형 및 개방형 질문에서 모델이 평가의 목적을 식별하는 능력도 무작위 추측을 훨씬 능가함을 확인하였습니다. 본 연구 결과는 최첨단 모델들이 이미 상당한 수준의 평가 인식 능력을 보유하고 있으나 아직 초인적 수준은 아님을 시사합니다. 향후 모델 개발 시 이 능력을 지속적으로 추적할 것을 권고합니다.
If AI models can detect when they are being evaluated, the effectiveness of evaluations might be compromised. For example, models could have systematically different behavior during evaluations, leading to less reliable benchmarks for deployment and governance decisions. We investigate whether frontier language models can accurately classify transcripts based on whether they originate from evaluations or real-world deployment, a capability we call evaluation awareness. To achieve this, we construct a diverse benchmark of 1,000 prompts and transcripts from 61 distinct datasets. These span public benchmarks (e.g., MMLU, SWEBench), real-world deployment interactions, and agent trajectories from scaffolding frameworks (e.g., web-browsing agents). Frontier models clearly demonstrate above-random evaluation awareness (Gemini-2.5-Pro reaches an AUC of 0.83), but do not yet surpass our simple human baseline (AUC of 0.92). Furthermore, both AI models and humans are better at identifying evaluations in agentic settings compared to chat settings. Additionally, we test whether models can identify the purpose of the evaluation. Under multiple-choice and open-ended questioning, AI models far outperform random chance in identifying what an evaluation is testing for. Our results indicate that frontier models already exhibit a substantial, though not yet superhuman, level of evaluation-awareness. We recommend tracking this capability in future models.
논문 링크
![]() 파이토치 한국 사용자 모임
파이토치 한국 사용자 모임![]() 이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일
이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일![]() 로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
![]() 아래
아래![]() 쪽에 좋아요
쪽에 좋아요![]() 를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~
를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~ ![]()