[2025/08/04 ~ 10] 이번 주에 살펴볼 만한 AI/ML 논문 모음
PyTorchKR



![]() 이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 첫째로 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 에이전트 시스템에서 비용 대비 성능 최적화에 대한 연구가 두드러집니다. 복잡한 다중 단계 작업을 수행하는 에이전트의 효율성을 높이면서도 운영 비용을 절감하려는 시도가 많으며, 이를 통해 AI 솔루션의 확장성과 접근성을 개선하려는 방향성이 명확합니다. 이는 산업 현장에서 AI 도입 시 현실적인 비용 문제를 해결하고, 보다 지속 가능한 AI 서비스 구축에 기여할 수 있는 중요한 연구 동향임을 보여줍니다.
이번 주 선정된 논문들을 살펴보면, 첫째로 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 에이전트 시스템에서 비용 대비 성능 최적화에 대한 연구가 두드러집니다. 복잡한 다중 단계 작업을 수행하는 에이전트의 효율성을 높이면서도 운영 비용을 절감하려는 시도가 많으며, 이를 통해 AI 솔루션의 확장성과 접근성을 개선하려는 방향성이 명확합니다. 이는 산업 현장에서 AI 도입 시 현실적인 비용 문제를 해결하고, 보다 지속 가능한 AI 서비스 구축에 기여할 수 있는 중요한 연구 동향임을 보여줍니다.
![]() 둘째로, 그래프 기반 지식 표현과 강화학습을 결합하여 에이전트의 추론 능력과 정보 검색 효율을 높이는 연구들이 눈에 띕니다. 단순한 텍스트 기반 검색을 넘어 엔티티와 관계를 구조화한 그래프 형태로 지식을 모델링하고, 이를 에이전트가 능동적으로 활용하도록 설계함으로써 복잡한 질의에 대한 정확도와 응답 품질을 향상시키고 있습니다. 이러한 접근은 에이전트가 더 깊이 있는 의미적 이해와 장기적 계획 수립을 가능하게 하여, AI의 지능적 상호작용 역량을 한층 강화하는 데 기여합니다.
둘째로, 그래프 기반 지식 표현과 강화학습을 결합하여 에이전트의 추론 능력과 정보 검색 효율을 높이는 연구들이 눈에 띕니다. 단순한 텍스트 기반 검색을 넘어 엔티티와 관계를 구조화한 그래프 형태로 지식을 모델링하고, 이를 에이전트가 능동적으로 활용하도록 설계함으로써 복잡한 질의에 대한 정확도와 응답 품질을 향상시키고 있습니다. 이러한 접근은 에이전트가 더 깊이 있는 의미적 이해와 장기적 계획 수립을 가능하게 하여, AI의 지능적 상호작용 역량을 한층 강화하는 데 기여합니다.
![]() 마지막으로, 다중 턴 대화에서의 도구 호출과 장기 기억 관리 문제를 해결하려는 연구가 활발합니다. 고정된 컨텍스트 윈도우의 한계를 극복하기 위해 단기 및 장기 기억을 효율적으로 관리하고, 동적으로 다양한 도구와 외부 API를 활용하는 에이전트 아키텍처가 제안되고 있습니다. 이는 실제 서비스 환경에서 사용자와의 지속적이고 복잡한 상호작용을 지원하며, 대규모 산업 시스템에서 낮은 지연 시간과 높은 신뢰성을 유지하는 데 필수적인 요소로 평가됩니다. 전반적으로 이번 주 논문들은 에이전트 AI가 실용적이고 확장 가능한 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 보여주고 있습니다.
마지막으로, 다중 턴 대화에서의 도구 호출과 장기 기억 관리 문제를 해결하려는 연구가 활발합니다. 고정된 컨텍스트 윈도우의 한계를 극복하기 위해 단기 및 장기 기억을 효율적으로 관리하고, 동적으로 다양한 도구와 외부 API를 활용하는 에이전트 아키텍처가 제안되고 있습니다. 이는 실제 서비스 환경에서 사용자와의 지속적이고 복잡한 상호작용을 지원하며, 대규모 산업 시스템에서 낮은 지연 시간과 높은 신뢰성을 유지하는 데 필수적인 요소로 평가됩니다. 전반적으로 이번 주 논문들은 에이전트 AI가 실용적이고 확장 가능한 방향으로 진화하고 있음을 보여주고 있습니다.
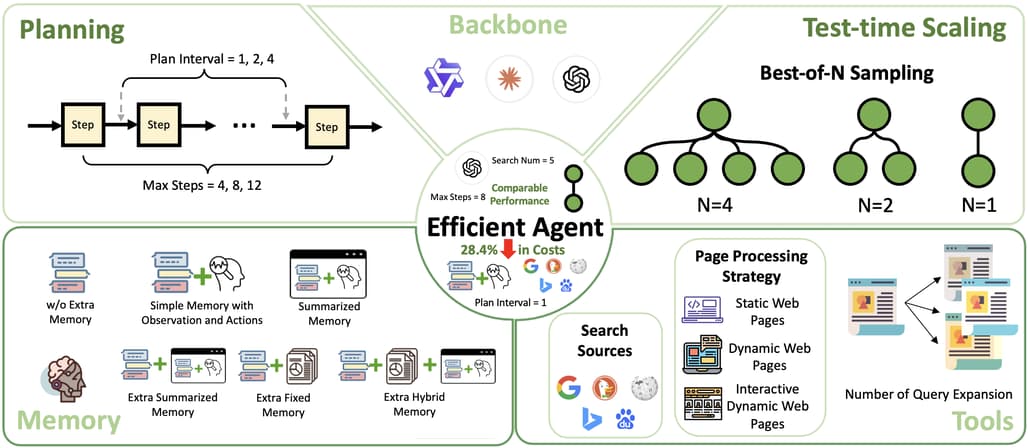
효율적인 에이전트: 비용 절감과 성능을 모두 갖춘 에이전트 설계 / Efficient Agents: Building Effective Agents While Reducing Cost
논문 소개
대규모 언어 모델(LLM) 기반 에이전트의 뛰어난 성능에도 불구하고 비용 증가가 확장성과 접근성을 저해하는 문제를 다루고 있습니다. 본 연구는 에이전트 시스템에서 효율성과 성능 간의 균형을 체계적으로 분석하며, 작업 복잡도, 추가 모듈의 효과 한계, 효율적인 프레임워크 설계가 비용 절감에 미치는 영향을 평가합니다. GAIA 벤치마크를 활용한 실험을 통해 LLM 백본 선택, 에이전트 프레임워크 구조, 테스트 시 확장 전략이 비용 대비 성능에 미치는 영향을 정량화하였습니다. 제안된 Efficient Agents 프레임워크는 기존 최고 수준의 오픈소스 에이전트 대비 약 3%의 성능 저하만으로 운영 비용을 28.4% 절감하여 비용 효율성을 크게 향상시켰습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대규모 언어 모델(LLM) 기반 에이전트의 뛰어난 능력은 복잡하고 다단계 작업을 수행하는 정교한 시스템을 가능하게 했으나, 증가하는 비용은 확장성과 접근성을 위협하고 있습니다. 본 연구는 성능을 희생하지 않으면서 비용 효율적인 설계의 필요성을 해결하기 위해 현대 에이전트 시스템에서 효율성과 효과성 간의 상충관계에 대한 최초의 체계적인 연구를 제시합니다. 우리는 세 가지 핵심 질문을 탐구합니다: (1) 에이전트 작업이 본질적으로 요구하는 복잡성은 어느 정도인가? (2) 추가 모듈이 언제부터 수익 체감 현상을 보이는가? (3) 효율적인 에이전트 프레임워크 설계를 통해 얼마나 많은 효율성을 얻을 수 있는가? GAIA 벤치마크에 대한 실증 분석을 통해 LLM 백본 선택, 에이전트 프레임워크 설계, 테스트 시 확장 전략의 영향을 평가하였습니다. cost-of-pass 지표를 활용하여 이들 요소 간의 효율성-성능 상충관계를 정량화하였습니다. 연구 결과는 작업 요구사항에 최적화된 복잡도를 갖는 새로운 에이전트 프레임워크인 Efficient Agents 개발에 기여합니다. Efficient Agents는 대표적인 오픈소스 에이전트 프레임워크인 OWL의 성능을 96.7% 유지하면서 운영 비용을 $0.398에서 $0.228로 절감하여 cost-of-pass를 28.4% 개선하였습니다. 본 연구는 효율적이고 고성능의 에이전트 시스템 설계를 위한 실질적인 통찰을 제공하며, AI 기반 솔루션의 접근성과 지속 가능성 향상에 기여합니다.
The remarkable capabilities of Large Language Model (LLM)-driven agents have enabled sophisticated systems to tackle complex, multi-step tasks, but their escalating costs threaten scalability and accessibility. This work presents the first systematic study of the efficiency-effectiveness trade-off in modern agent systems, addressing the critical need for cost-effective designs without sacrificing performance. We investigate three key questions: (1) How much complexity do agentic tasks inherently require? (2) When do additional modules yield diminishing returns? (3) How much efficiency can be gained through the design of efficient agent frameworks? Through an empirical analysis on the GAIA benchmark, we evaluate the impact of LLM backbone selection, agent framework designs, and test-time scaling strategies. Using the cost-of-pass metric, we quantify the efficiency-performance trade-off across these dimensions. Our findings inform the development of Efficient Agents , a novel agent framework that has an optimal complexity to task requirements. Efficient Agents retains 96.7% of the performance of OWL, one leading open-source agent framework, while reducing operational costs from $0.398 to $0.228, resulting in a 28.4% improvement in cost-of-pass. Our work provides actionable insights for designing efficient, high-performing agent systems, advancing the accessibility and sustainability of AI-driven solutions.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/OPPO-PersonalAI/OAgents
Graph-R1: 종단 간 강화학습 기반 에이전트형 그래프RAG 프레임워크 연구 / Graph-R1: Towards Agentic GraphRAG Framework via End-to-end Reinforcement Learning
논문 소개
Graph-R1은 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)의 환각 문제를 완화하기 위해 외부 지식을 활용하는 기존 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 방식의 한계를 극복하고자 제안된 강화학습 기반 에이전트형 그래프 RAG 프레임워크입니다. 이 방법은 경량화된 하이퍼그래프 지식 구조를 구축하고, 다회차 에이전트-환경 상호작용으로 검색 과정을 모델링하며, 보상 신호를 통한 종단간(end-to-end) 최적화를 수행합니다. 실험 결과, Graph-R1은 기존의 그래프 RAG 및 강화학습 적용 RAG 기법 대비 추론 정확도, 검색 효율성, 생성 품질에서 우수한 성능을 보였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
검색-증강 생성(RAG)은 외부 지식을 통합하여 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)에서 발생하는 환각 현상을 완화하지만, 구조적 의미가 부족한 청크 기반 검색에 의존합니다. GraphRAG 방법은 지식을 개체-관계 그래프로 모델링하여 RAG를 개선하지만, 높은 구축 비용, 고정된 일회성 검색, 그리고 장기 문맥 추론 및 프롬프트 설계에 대한 의존성이라는 문제에 직면해 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, 본 논문에서는 종단 간 강화 학습(RL)을 활용한 에이전트 기반 GraphRAG 프레임워크인 Graph-R1을 제안합니다. Graph-R1은 경량 지식 하이퍼그래프 구축을 도입하고, 검색을 다회차 에이전트-환경 상호작용으로 모델링하며, 종단 간 보상 메커니즘을 통해 에이전트 프로세스를 최적화합니다. 표준 RAG 데이터셋에서의 실험 결과, Graph-R1은 기존 GraphRAG 및 RL 강화 RAG 방법들에 비해 추론 정확도, 검색 효율성, 생성 품질에서 우수한 성능을 보였습니다.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) mitigates hallucination in LLMs by incorporating external knowledge, but relies on chunk-based retrieval that lacks structural semantics. GraphRAG methods improve RAG by modeling knowledge as entity-relation graphs, but still face challenges in high construction cost, fixed one-time retrieval, and reliance on long-context reasoning and prompt design. To address these challenges, we propose Graph-R1, an agentic GraphRAG framework via end-to-end reinforcement learning (RL). It introduces lightweight knowledge hypergraph construction, models retrieval as a multi-turn agent-environment interaction, and optimizes the agent process via an end-to-end reward mechanism. Experiments on standard RAG datasets show that Graph-R1 outperforms traditional GraphRAG and RL-enhanced RAG methods in reasoning accuracy, retrieval efficiency, and generation quality.
논문 링크
TURA: 도구 보강 통합 검색 에이전트를 활용한 AI 검색 혁신 / TURA: Tool-Augmented Unified Retrieval Agent for AI Search
논문 소개
대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 기존의 검색 엔진은 주로 정적인 웹 문서 기반의 Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG) 방식을 사용하지만, 실시간 정보나 동적 데이터 처리에는 한계가 있습니다. TURA는 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 RAG와 에이전트 기반 도구 활용을 결합한 3단계 프레임워크로, 쿼리 분해 및 정보원 검색, DAG(유향 비순환 그래프) 기반 작업 계획, 경량화된 에이전트 실행기를 포함합니다. 이를 통해 정적 콘텐츠와 실시간 API, 데이터베이스 등 동적 정보원을 통합하여 대규모 산업 환경에서 저지연으로 실시간 응답을 제공합니다. TURA는 수천만 사용자에게 안정적이고 신속한 AI 검색 서비스를 제공하는 최초의 통합 아키텍처입니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)의 출현은 주로 웹 코퍼스 기반의 검색-증강 생성(RAG)을 활용하여 검색 엔진을 대화형 AI 검색 제품으로 변화시키고 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 패러다임은 산업적 측면에서 중요한 한계를 지니고 있습니다. 전통적인 RAG 접근법은 실시간 요구사항과 티켓 가용성 또는 재고와 같이 동적으로 생성되는 콘텐츠에 접근해야 하는 구조화된 쿼리에 대응하는 데 어려움을 겪습니다. 정적인 페이지 인덱싱에 한정된 검색 엔진은 이러한 시의성 있는 데이터에 필요한 상호작용 쿼리를 수행할 수 없습니다. 학계 연구는 정적 콘텐츠에 최적화된 RAG에 집중해 왔으며, 복잡한 의도와 데이터베이스 및 실시간 API와 같은 동적 소스의 필요성은 간과되어 왔습니다. 이러한 격차를 해소하기 위해, 본 논문에서는 정적 콘텐츠와 동적 실시간 정보를 모두 활용할 수 있도록 RAG와 에이전트 기반 도구 사용을 결합한 새로운 3단계 프레임워크인 TURA(도구 증강 통합 검색 에이전트)를 제안합니다. TURA는 세 가지 핵심 구성 요소로 이루어져 있습니다: 쿼리를 분해하고 Model Context Protocol(MCP) 서버로 캡슐화된 정보 소스를 검색하는 의도 인식 검색 모듈, 작업 의존성을 방향성 비순환 그래프(DAG)로 모델링하여 최적의 병렬 실행을 지원하는 DAG 기반 작업 계획자, 그리고 효율적인 도구 호출을 위한 경량화된 증류 에이전트 실행기입니다. TURA는 정적 RAG와 동적 정보 소스 간의 격차를 체계적으로 연결한 최초의 아키텍처로서, 세계적 수준의 AI 검색 제품을 구현합니다. 수천만 명의 사용자에게 서비스를 제공하며, 에이전트 기반 프레임워크를 활용해 대규모 산업 시스템의 저지연 요구를 충족하면서도 견고하고 실시간 응답을 제공합니다.
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) is transforming search engines into conversational AI search products, primarily using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) on web corpora. However, this paradigm has significant industrial limitations. Traditional RAG approaches struggle with real-time needs and structured queries that require accessing dynamically generated content like ticket availability or inventory. Limited to indexing static pages, search engines cannot perform the interactive queries needed for such time-sensitive data. Academic research has focused on optimizing RAG for static content, overlooking complex intents and the need for dynamic sources like databases and real-time APIs. To bridge this gap, we introduce TURA (Tool-Augmented Unified Retrieval Agent for AI Search), a novel three-stage framework that combines RAG with agentic tool-use to access both static content and dynamic, real-time information. TURA has three key components: an Intent-Aware Retrieval module to decompose queries and retrieve information sources encapsulated as Model Context Protocol (MCP) Servers, a DAG-based Task Planner that models task dependencies as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) for optimal parallel execution, and a lightweight Distilled Agent Executor for efficient tool calling. TURA is the first architecture to systematically bridge the gap between static RAG and dynamic information sources for a world-class AI search product. Serving tens of millions of users, it leverages an agentic framework to deliver robust, real-time answers while meeting the low-latency demands of a large-scale industrial system.
논문 링크
자가 진화 에이전트 서베이: 인공 초지능으로 가는 길 / A Survey of Self-Evolving Agents: On Path to Artificial Super Intelligence

논문 소개
대형 언어 모델(LLM)은 뛰어난 성능을 보이나 내부 파라미터를 실시간으로 적응시키지 못하는 정적인 한계가 있다. 이에 따라 지속적인 학습과 적응이 가능한 자기 진화 에이전트(self-evolving agents)에 대한 연구가 활발해지고 있으며, 본 서베이는 진화 대상, 시기, 방법의 세 가지 핵심 차원에서 이들을 체계적으로 분석한다. 에이전트 구성 요소별 진화 메커니즘, 적응 단계별 방법론, 알고리즘 및 아키텍처 설계, 평가 지표와 벤치마크, 그리고 다양한 응용 분야를 포괄적으로 다룬다. 또한 안전성, 확장성, 공진화 동역학 등 주요 도전 과제와 연구 방향을 제시하며, 궁극적으로 인간 수준을 뛰어넘는 인공 초지능(ASI) 실현을 위한 로드맵을 제공한다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 언어 모델(LLM)은 뛰어난 성능을 보여주었으나, 본질적으로 정적인 특성을 지니고 있어 내부 파라미터를 새로운 과제, 변화하는 지식 영역, 또는 동적인 상호작용 환경에 맞추어 적응시키지 못합니다. LLM이 점점 더 개방형의 상호작용 환경에 배치됨에 따라 이러한 정적 특성은 중요한 병목 현상이 되었으며, 실시간으로 적응적 추론, 행동, 진화를 수행할 수 있는 에이전트의 필요성이 대두되고 있습니다. 이러한 패러다임 전환—정적 모델의 확장에서 자기진화 에이전트 개발로의 변화—은 데이터, 상호작용, 경험으로부터 지속적인 학습과 적응을 가능하게 하는 아키텍처 및 방법에 대한 관심을 증대시켰습니다. 본 서베이 논문은 자기진화 에이전트에 관한 최초의 체계적이고 포괄적인 리뷰를 제공하며, ‘무엇을 진화시킬 것인가’, ‘언제 진화시킬 것인가’, ‘어떻게 진화시킬 것인가’라는 세 가지 기본 차원을 중심으로 구성되어 있습니다. 우리는 에이전트 구성 요소(예: 모델, 메모리, 도구, 아키텍처) 전반에 걸친 진화 메커니즘을 검토하고, 적응 방법을 단계별(예: 테스트 내 시간, 테스트 간 시간)로 분류하며, 진화적 적응을 이끄는 알고리즘 및 아키텍처 설계(예: 스칼라 보상, 텍스트 피드백, 단일 에이전트 및 다중 에이전트 시스템)를 분석합니다. 또한, 자기진화 에이전트에 특화된 평가 지표와 벤치마크를 분석하고, 코딩, 교육, 헬스케어 등 다양한 분야에서의 응용 사례를 조명하며, 안전성, 확장성, 공진화 역학과 관련된 주요 도전과 연구 방향을 제시합니다. 본 서베이는 자기진화 에이전트를 이해하고 설계하기 위한 구조화된 프레임워크를 제공함으로써, 연구 및 실제 배포에서 적응형 에이전트 시스템 발전을 위한 로드맵을 확립하며, 궁극적으로 에이전트가 자율적으로 진화하여 광범위한 과제에서 인간 수준 이상의 지능을 발휘하는 인공 초지능(ASI)의 실현을 위한 길을 밝히고자 합니다.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities but remain fundamentally static, unable to adapt their internal parameters to novel tasks, evolving knowledge domains, or dynamic interaction contexts. As LLMs are increasingly deployed in open-ended, interactive environments, this static nature has become a critical bottleneck, necessitating agents that can adaptively reason, act, and evolve in real time. This paradigm shift -- from scaling static models to developing self-evolving agents -- has sparked growing interest in architectures and methods enabling continual learning and adaptation from data, interactions, and experiences. This survey provides the first systematic and comprehensive review of self-evolving agents, organized around three foundational dimensions -- what to evolve, when to evolve, and how to evolve. We examine evolutionary mechanisms across agent components (e.g., models, memory, tools, architecture), categorize adaptation methods by stages (e.g., intra-test-time, inter-test-time), and analyze the algorithmic and architectural designs that guide evolutionary adaptation (e.g., scalar rewards, textual feedback, single-agent and multi-agent systems). Additionally, we analyze evaluation metrics and benchmarks tailored for self-evolving agents, highlight applications in domains such as coding, education, and healthcare, and identify critical challenges and research directions in safety, scalability, and co-evolutionary dynamics. By providing a structured framework for understanding and designing self-evolving agents, this survey establishes a roadmap for advancing adaptive agentic systems in both research and real-world deployments, ultimately shedding lights to pave the way for the realization of Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), where agents evolve autonomously, performing at or beyond human-level intelligence across a wide array of tasks.
논문 링크
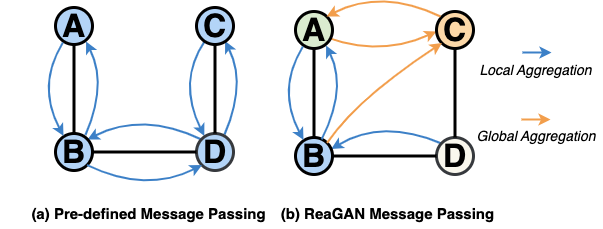
ReaGAN: 에이전트 기반 노드 추론 그래프 에이전틱 네트워크 / ReaGAN: Node-as-Agent-Reasoning Graph Agentic Network
논문 소개
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)의 기존 고정된 정보 전달 방식은 노드 간 정보 불균형과 전역 의미 관계 반영의 한계를 가지고 있습니다. ReaGAN은 각 노드를 독립적인 에이전트로 설정하여 내부 메모리를 기반으로 자율적 의사결정과 계획 수립을 가능하게 하며, 적응적인 메시지 전달을 구현합니다. 또한, 검색 보강 생성(Retrieval-augmented generation, RAG)을 통해 노드가 전역적 의미 연관 정보를 활용할 수 있도록 하여 그래프 내 장거리 관계를 효과적으로 포착합니다. 이 방법은 미세 조정 없이 고정된 대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용해 소수 샷 학습 환경에서도 경쟁력 있는 성능을 보여줍니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
그래프 신경망(Graph Neural Networks, GNN)은 미리 정의된 집계 메커니즘을 통해 이웃 노드 간 정보를 전파함으로써 그래프 기반 학습에서 뛰어난 성과를 거두었습니다. 그러나 이러한 고정된 방식은 두 가지 주요 한계를 지닙니다. 첫째, 노드 정보량의 불균형을 처리하지 못하는데, 일부 노드는 풍부한 정보를 가지는 반면 다른 노드는 희박한 정보를 가집니다. 둘째, 미리 정의된 메시지 전달은 주로 국소 구조적 유사성에 의존하며 그래프 전반에 걸친 전역 의미 관계를 무시하여, 멀리 떨어져 있지만 관련 있는 정보를 포착하는 모델의 능력을 제한합니다. 본 논문에서는 각 노드에 자율적인 노드 수준 의사결정 능력을 부여하는 에이전트 기반 프레임워크인 Retrieval-augmented Graph Agentic Network (ReaGAN)을 제안합니다. 각 노드는 내부 메모리를 바탕으로 독립적으로 다음 행동을 계획하는 에이전트로 작동하여 노드 수준의 계획 및 적응적 메시지 전파를 가능하게 합니다. 또한, 검색-증강 생성(Retrieval-augmented Generation, RAG)을 통해 노드가 의미적으로 관련된 콘텐츠에 접근하고 그래프 내 전역 관계를 구축할 수 있습니다. ReaGAN은 파인튜닝 없이 고정된 LLM 백본을 사용하여 소수 샷 인컨텍스트 학습(few-shot in-context) 환경에서 경쟁력 있는 성능을 달성하며, 그래프 학습에서 에이전트 기반 계획과 국소-전역 검색의 가능성을 보여줍니다.
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved remarkable success in graph-based learning by propagating information among neighbor nodes via predefined aggregation mechanisms. However, such fixed schemes often suffer from two key limitations. First, they cannot handle the imbalance in node informativeness -- some nodes are rich in information, while others remain sparse. Second, predefined message passing primarily leverages local structural similarity while ignoring global semantic relationships across the graph, limiting the model's ability to capture distant but relevant information. We propose Retrieval-augmented Graph Agentic Network (ReaGAN), an agent-based framework that empowers each node with autonomous, node-level decision-making. Each node acts as an agent that independently plans its next action based on its internal memory, enabling node-level planning and adaptive message propagation. Additionally, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) allows nodes to access semantically relevant content and build global relationships in the graph. ReaGAN achieves competitive performance under few-shot in-context settings using a frozen LLM backbone without fine-tuning, showcasing the potential of agentic planning and local-global retrieval in graph learning.
논문 링크
MemTool: 다중 대화 LLM 에이전트에서 동적 도구 호출을 위한 단기 메모리 관리 최적화 / MemTool: Optimizing Short-Term Memory Management for Dynamic Tool Calling in LLM Agent Multi-Turn Conversations
논문 소개
대형 언어 모델(LLM) 에이전트는 개별 쿼리에 맞춰 동적으로 도구나 MCP 서버를 탐색하고 활용하는 능력을 갖추었으나, 고정된 컨텍스트 윈도우는 반복적이고 독립적인 도구 사용이 필요한 다중 대화(turn) 상황에서 한계가 있습니다. MemTool은 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 LLM 에이전트가 다중 대화 중 도구 및 MCP 서버 컨텍스트를 동적으로 관리할 수 있는 단기 메모리 프레임워크를 제안합니다. 세 가지 에이전트 아키텍처(자율 에이전트 모드, 워크플로우 모드, 하이브리드 모드)를 통해 다양한 제어 수준과 자율성을 제공하며, 13개 이상의 LLM을 대상으로 한 실험에서 각 모드별 도구 제거 효율성과 작업 완성도를 평가하였습니다. 결과적으로 자율 모드는 고성능 모델에서 높은 메모리 효율을 보였고, 워크플로우와 하이브리드 모드는 안정적인 도구 관리와 높은 작업 완성도를 달성하는 등 각 모드별 특성과 활용 방안에 대한 실용적 권고를 제시합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 언어 모델(LLM) 에이전트는 개별 쿼리에 대해 관련 도구 또는 모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜(Model Context Protocol, MCP) 서버를 동적으로 탐색하고 통합하는 뛰어난 자율적 능력을 보여주었습니다. 그러나 고정된 컨텍스트 윈도우는 반복적이고 독립적인 도구 사용이 필요한 다중 턴 상호작용에서 효율성을 제한합니다. 본 논문에서는 LLM 에이전트가 다중 턴 대화 전반에 걸쳐 도구 또는 MCP 서버 컨텍스트를 동적으로 관리할 수 있도록 하는 단기 메모리 프레임워크인 MemTool을 제안합니다. MemTool은 세 가지 에이전트 아키텍처를 제공합니다: 1) 완전한 도구 관리 자율성을 부여하는 자율 에이전트 모드, 2) 자율성 없이 결정론적 제어를 제공하는 워크플로우 모드, 3) 자율성과 결정론적 제어를 결합한 하이브리드 모드. ScaleMCP 벤치마크에서 13개 이상의 LLM을 대상으로 각 MemTool 모드를 평가하였으며, 100회 연속 사용자 상호작용 실험을 통해 도구 제거 비율(단기 메모리 효율성)과 작업 완료 정확도를 측정하였습니다. 자율 에이전트 모드에서는 추론형 LLM이 높은 도구 제거 효율성(3-윈도우 평균 90-94%)을 달성한 반면, 중간 규모 모델은 현저히 낮은 효율성(0-60%)을 보였습니다. 워크플로우 및 하이브리드 모드는 일관되게 도구 제거를 효과적으로 관리하였으며, 자율 및 하이브리드 모드는 작업 완료에서 우수한 성능을 보였습니다. 본 논문에서는 작업 정확도, 에이전시, 모델 역량을 기반으로 각 MemTool 모드의 트레이드오프와 권장 사항을 제시합니다.
Large Language Model (LLM) agents have shown significant autonomous capabilities in dynamically searching and incorporating relevant tools or Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers for individual queries. However, fixed context windows limit effectiveness in multi-turn interactions requiring repeated, independent tool usage. We introduce MemTool, a short-term memory framework enabling LLM agents to dynamically manage tools or MCP server contexts across multi-turn conversations. MemTool offers three agentic architectures: 1) Autonomous Agent Mode, granting full tool management autonomy, 2) Workflow Mode, providing deterministic control without autonomy, and 3) Hybrid Mode, combining autonomous and deterministic control. Evaluating each MemTool mode across 13+ LLMs on the ScaleMCP benchmark, we conducted experiments over 100 consecutive user interactions, measuring tool removal ratios (short-term memory efficiency) and task completion accuracy. In Autonomous Agent Mode, reasoning LLMs achieve high tool-removal efficiency (90-94% over a 3-window average), while medium-sized models exhibit significantly lower efficiency (0-60%). Workflow and Hybrid modes consistently manage tool removal effectively, whereas Autonomous and Hybrid modes excel at task completion. We present trade-offs and recommendations for each MemTool mode based on task accuracy, agency, and model capabilities.
논문 링크
에이전트 기반 웹: AI 에이전트와 함께하는 차세대 웹 구축 / Agentic Web: Weaving the Next Web with AI Agents
논문 소개
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)을 기반으로 한 AI 에이전트의 등장은 자율적이고 목표 지향적인 상호작용이 중심이 되는 에이전트 웹(Agentic Web)이라는 새로운 인터넷 패러다임을 제시합니다. 이 패러다임에서는 에이전트들이 사용자 대신 복잡한 작업을 계획, 조정, 실행하며, 인간 중심의 상호작용에서 기계 간 상호작용으로 전환되어 반복적인 디지털 작업 부담을 경감합니다. 논문은 지능, 상호작용, 경제성의 세 가지 핵심 차원으로 구성된 개념 모델을 통해 에이전트 웹의 기술적 기반과 발전 과정을 체계적으로 분석하고, 확장 가능한 에이전트 시스템 구축을 위한 아키텍처 및 인프라 도전 과제를 다룹니다. 또한, 에이전트 웹의 응용 가능성과 사회적 위험, 거버넌스 문제를 논의하며, 인간 의도와 자율 에이전트 행동이 조화된 개방적이고 안전한 생태계 개발을 위한 연구 방향을 제시합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
AI 에이전트가 대형 언어 모델(LLM)에 의해 구동되면서, 자율적이고 목표 지향적인 상호작용으로 정의되는 인터넷의 새로운 단계인 에이전틱 웹(Agentic Web)으로의 중대한 전환이 이루어지고 있습니다. 이 패러다임에서 에이전트들은 사용자 대신 복잡한 작업을 계획하고 조율하며 실행하기 위해 서로 직접 상호작용합니다. 인간 중심의 상호작용에서 기계 간 상호작용으로의 전환은 의도를 위임할 수 있게 하여, 사용자가 일상적인 디지털 작업에서 해방되고 보다 상호작용적이며 자동화된 웹 경험을 가능하게 합니다. 본 논문에서는 에이전틱 웹을 이해하고 구축하기 위한 체계적인 프레임워크를 제시합니다. PC 및 모바일 웹 시대에서부터의 진화를 추적하고, 이러한 전환을 뒷받침하는 핵심 기술적 기반을 규명합니다. 본 프레임워크의 중심에는 지능(intelligence), 상호작용(interaction), 경제학(economics)이라는 세 가지 주요 차원으로 구성된 개념적 모델이 있습니다. 이 차원들은 검색, 추천, 계획, 협업 등 AI 에이전트의 역량을 총체적으로 가능하게 합니다. 또한, 통신 프로토콜, 오케스트레이션 전략, 에이전트 어텐션 경제(Agent Attention Economy)와 같은 신흥 패러다임을 포함하여 확장 가능한 에이전틱 시스템 구축에 따른 아키텍처 및 인프라 도전 과제를 분석합니다. 마지막으로, 에이전틱 시스템이 가져올 잠재적 응용 분야, 사회적 위험, 거버넌스 문제를 논의하고, 인간의 의도와 자율 에이전트 행동이 함께 형성하는 개방적이고 안전하며 지능적인 생태계 개발을 위한 연구 방향을 제시합니다. 에이전틱 웹 관련 최신 연구 모음은 다음 저장소에서 지속적으로 업데이트되고 있습니다: GitHub - SafeRL-Lab/agentic-web: Agentic Web: Weaving the Next Web with AI Agents..
The emergence of AI agents powered by large language models (LLMs) marks a pivotal shift toward the Agentic Web, a new phase of the internet defined by autonomous, goal-driven interactions. In this paradigm, agents interact directly with one another to plan, coordinate, and execute complex tasks on behalf of users. This transition from human-driven to machine-to-machine interaction allows intent to be delegated, relieving users from routine digital operations and enabling a more interactive, automated web experience. In this paper, we present a structured framework for understanding and building the Agentic Web. We trace its evolution from the PC and Mobile Web eras and identify the core technological foundations that support this shift. Central to our framework is a conceptual model consisting of three key dimensions: intelligence, interaction, and economics. These dimensions collectively enable the capabilities of AI agents, such as retrieval, recommendation, planning, and collaboration. We analyze the architectural and infrastructural challenges involved in creating scalable agentic systems, including communication protocols, orchestration strategies, and emerging paradigms such as the Agent Attention Economy. We conclude by discussing the potential applications, societal risks, and governance issues posed by agentic systems, and outline research directions for developing open, secure, and intelligent ecosystems shaped by both human intent and autonomous agent behavior. A continuously updated collection of relevant studies for agentic web is available at: GitHub - SafeRL-Lab/agentic-web: Agentic Web: Weaving the Next Web with AI Agents..
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/SafeRL-Lab/agentic-web
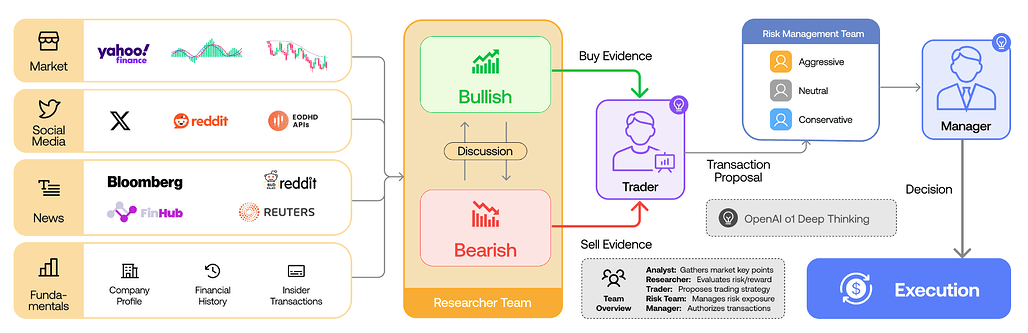
TradingAgents: 다중 에이전트 LLM 기반 금융 트레이딩 프레임워크 / TradingAgents: Multi-Agents LLM Financial Trading Framework
논문 소개
TradingAgents는 대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 활용한 다중 에이전트 기반 금융 주식 거래 프레임워크로, 실제 트레이딩 회사의 협업 구조를 모방하여 각기 다른 역할을 수행하는 전문화된 에이전트들(기본적 분석가, 감성 분석가, 기술적 분석가, 다양한 위험 프로필의 트레이더 등)로 구성되어 있습니다. 시장 상황을 평가하는 Bull과 Bear 연구원, 위험 노출을 감시하는 리스크 관리 팀, 그리고 토론과 과거 데이터를 종합해 의사결정을 내리는 트레이더들이 유기적으로 협력하는 동적 환경을 시뮬레이션합니다. 이 프레임워크는 누적 수익률, 샤프 비율(Sharpe ratio), 최대 낙폭(maximum drawdown) 등에서 기존 모델 대비 우수한 성능을 보이며, 금융 거래에서 다중 에이전트 LLM 시스템의 가능성을 입증합니다. 소스 코드는 공개되어 있어 연구 및 실무 적용에 활용할 수 있습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
자동화된 문제 해결 분야에서 대형 언어 모델(LLM)을 기반으로 한 에이전트 집단을 활용한 상당한 진전이 이루어졌습니다. 금융 분야에서는 주로 특정 작업을 수행하는 단일 에이전트 시스템이나 독립적으로 데이터를 수집하는 다중 에이전트 프레임워크에 집중해왔습니다. 그러나 다중 에이전트 시스템이 실제 거래 회사의 협력적 역학을 재현할 수 있는 잠재력은 아직 충분히 탐구되지 않았습니다. TradingAgents는 거래 회사를 모티브로 한 새로운 주식 거래 프레임워크를 제안하며, 기본적 분석가, 감성 분석가, 기술적 분석가, 그리고 다양한 위험 프로필을 가진 트레이더 등 전문화된 역할을 수행하는 LLM 기반 에이전트들로 구성됩니다. 이 프레임워크에는 시장 상황을 평가하는 Bull 및 Bear 연구원 에이전트, 노출을 모니터링하는 리스크 관리 팀, 그리고 토론과 과거 데이터를 종합하여 정보에 기반한 결정을 내리는 트레이더들이 포함되어 있습니다. 동적이고 협력적인 거래 환경을 시뮬레이션함으로써 거래 성과 향상을 목표로 합니다. 상세한 아키텍처와 광범위한 실험 결과는 누적 수익률, 샤프 비율, 최대 낙폭에서 기준 모델 대비 우수성을 입증하며, 금융 거래에서 다중 에이전트 LLM 프레임워크의 가능성을 강조합니다. TradingAgents는 GitHub - TauricResearch/TradingAgents: TradingAgents: Multi-Agents LLM Financial Trading Framework 에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
Significant progress has been made in automated problem-solving using societies of agents powered by large language models (LLMs). In finance, efforts have largely focused on single-agent systems handling specific tasks or multi-agent frameworks independently gathering data. However, the multi-agent systems' potential to replicate real-world trading firms' collaborative dynamics remains underexplored. TradingAgents proposes a novel stock trading framework inspired by trading firms, featuring LLM-powered agents in specialized roles such as fundamental analysts, sentiment analysts, technical analysts, and traders with varied risk profiles. The framework includes Bull and Bear researcher agents assessing market conditions, a risk management team monitoring exposure, and traders synthesizing insights from debates and historical data to make informed decisions. By simulating a dynamic, collaborative trading environment, this framework aims to improve trading performance. Detailed architecture and extensive experiments reveal its superiority over baseline models, with notable improvements in cumulative returns, Sharpe ratio, and maximum drawdown, highlighting the potential of multi-agent LLM frameworks in financial trading. TradingAgents is available at GitHub - TauricResearch/TradingAgents: TradingAgents: Multi-Agents LLM Financial Trading Framework.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/TauricResearch/TradingAgents
워크플로우 그래프로 구현하는 실무용 생산 등급 대화 에이전트 구축 방법 / A Practical Approach for Building Production-Grade Conversational Agents with Workflow Graphs
논문 소개
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)의 발전은 검색, 추천, 챗봇 등 다양한 서비스 분야에서 성능 향상을 가져왔으나, 산업 현장에 적용할 때는 유연한 대화 능력과 서비스별 제약 조건 준수라는 상충되는 요구사항을 동시에 만족시켜야 하는 어려움이 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위한 실용적인 접근법과 실제 전자상거래 도메인에 적용한 대화 에이전트 구축 과정을 상세히 소개합니다. 제안된 워크플로우 그래프(workflow graphs) 기반 프레임워크는 확장성, 제어 가능성, 신뢰성을 갖춘 AI 대화 시스템 개발에 기여하며, 학계 연구와 산업 적용 간 간극을 줄이는 데 유용한 인사이트를 제공합니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 발전은 검색, 추천, 챗봇 애플리케이션 등 다양한 서비스 분야에서 상당한 개선을 가져왔습니다. 그러나 최첨단(SOTA) 연구를 산업 현장에 적용하는 데에는 유연한 대화 능력을 유지함과 동시에 서비스별 제약 조건을 엄격히 준수해야 하는 어려움이 존재합니다. 이는 LLM의 확률적 특성으로 인해 상충되는 두 가지 요구사항으로 볼 수 있습니다. 본 논문에서는 이러한 도전 과제를 해결하기 위한 당사의 접근법을 제안하고, 실제 응용에서 내재된 한계를 극복하기 위해 적용한 전략들을 상세히 기술합니다. 전자상거래 도메인을 대상으로 설계된 대화형 에이전트의 실무 사례 연구를 수행하며, 구현 워크플로우와 최적화 과정을 구체적으로 설명합니다. 본 연구 결과는 학술 연구와 실제 응용 간의 간극을 해소하는 통찰을 제공하며, 확장 가능하고 제어 가능하며 신뢰할 수 있는 AI 기반 에이전트 개발을 위한 프레임워크를 제시합니다.
The advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to significant improvements in various service domains, including search, recommendation, and chatbot applications. However, applying state-of-the-art (SOTA) research to industrial settings presents challenges, as it requires maintaining flexible conversational abilities while also strictly complying with service-specific constraints. This can be seen as two conflicting requirements due to the probabilistic nature of LLMs. In this paper, we propose our approach to addressing this challenge and detail the strategies we employed to overcome their inherent limitations in real-world applications. We conduct a practical case study of a conversational agent designed for the e-commerce domain, detailing our implementation workflow and optimizations. Our findings provide insights into bridging the gap between academic research and real-world application, introducing a framework for developing scalable, controllable, and reliable AI-driven agents.
논문 링크
Mem0: 확장 가능한 장기 메모리를 갖춘 실전용 AI 에이전트 구축 / Mem0: Building Production-Ready AI Agents with Scalable Long-Term Memory
논문 소개
Mem0는 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)의 고정된 문맥 창 한계를 극복하기 위해 동적으로 중요한 정보를 추출, 통합, 검색하는 확장 가능한 메모리 중심 아키텍처를 제안합니다. 그래프 기반 메모리 표현을 활용한 확장 버전은 대화 요소 간 복잡한 관계 구조를 효과적으로 포착합니다. LOCOMO 벤치마크 평가에서 Mem0는 기존 메모리 시스템 대비 단일-홉, 시간적, 다중-홉, 개방형 질문 등 다양한 유형에서 우수한 성능을 보이며, 특히 OpenAI 대비 26% 상대적 성능 향상을 기록했습니다. 또한 전체 문맥 처리 방식에 비해 계산 비용과 지연 시간을 크게 줄여 실용적인 AI 에이전트 구축에 적합함을 입증하였습니다.
논문 초록(Abstract)
대형 언어 모델(LLM)은 문맥상 일관된 응답 생성에서 뛰어난 성능을 보였으나, 고정된 컨텍스트 윈도우는 장기간 다중 세션 대화에서 일관성을 유지하는 데 근본적인 한계를 야기합니다. 본 논문에서는 진행 중인 대화에서 중요한 정보를 동적으로 추출, 통합, 검색하는 확장 가능한 메모리 중심 아키텍처인 Mem0를 제안합니다. 이를 기반으로 대화 요소 간 복잡한 관계 구조를 포착하기 위해 그래프 기반 메모리 표현을 활용한 향상된 변형도 함께 제시합니다. LOCOMO 벤치마크에서의 종합 평가를 통해, 본 연구는 다음 여섯 가지 기준군과 체계적으로 비교하였습니다: (i) 기존의 메모리 증강 시스템, (ii) 다양한 청크 크기와 k값을 적용한 검색-증강 생성(RAG), (iii) 전체 대화 기록을 처리하는 풀 컨텍스트 접근법, (iv) 오픈소스 메모리 솔루션, (v) 독점 모델 시스템, (vi) 전용 메모리 관리 플랫폼. 실험 결과, 제안한 방법들은 단일 홉, 시간적, 다중 홉, 오픈 도메인 등 네 가지 질문 유형 전반에서 모든 기존 메모리 시스템을 일관되게 능가함을 확인하였습니다. 특히 Mem0는 LLM-as-a-Judge 지표에서 OpenAI 대비 26% 상대적 향상을 달성하였으며, 그래프 메모리를 적용한 Mem0는 기본 구성 대비 전체 점수가 약 2% 더 높았습니다. 정확도 향상뿐만 아니라, 풀 컨텍스트 방식에 비해 계산 비용도 현저히 절감하였습니다. 구체적으로 Mem0는 p95 지연 시간을 91% 단축하고 토큰 비용을 90% 이상 절감하여, 고도화된 추론 능력과 실용적 배포 제약 간의 균형을 효과적으로 제공합니다. 본 연구 결과는 장기 대화 일관성을 위한 구조화되고 지속적인 메모리 메커니즘의 중요성을 부각하며, 보다 신뢰할 수 있고 효율적인 LLM 기반 AI 에이전트 개발의 길을 열어줍니다.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable prowess in generating contextually coherent responses, yet their fixed context windows pose fundamental challenges for maintaining consistency over prolonged multi-session dialogues. We introduce Mem0, a scalable memory-centric architecture that addresses this issue by dynamically extracting, consolidating, and retrieving salient information from ongoing conversations. Building on this foundation, we further propose an enhanced variant that leverages graph-based memory representations to capture complex relational structures among conversational elements. Through comprehensive evaluations on LOCOMO benchmark, we systematically compare our approaches against six baseline categories: (i) established memory-augmented systems, (ii) retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with varying chunk sizes and k-values, (iii) a full-context approach that processes the entire conversation history, (iv) an open-source memory solution, (v) a proprietary model system, and (vi) a dedicated memory management platform. Empirical results show that our methods consistently outperform all existing memory systems across four question categories: single-hop, temporal, multi-hop, and open-domain. Notably, Mem0 achieves 26% relative improvements in the LLM-as-a-Judge metric over OpenAI, while Mem0 with graph memory achieves around 2% higher overall score than the base configuration. Beyond accuracy gains, we also markedly reduce computational overhead compared to full-context method. In particular, Mem0 attains a 91% lower p95 latency and saves more than 90% token cost, offering a compelling balance between advanced reasoning capabilities and practical deployment constraints. Our findings highlight critical role of structured, persistent memory mechanisms for long-term conversational coherence, paving the way for more reliable and efficient LLM-driven AI agents.
논문 링크
더 읽어보기
https://github.com/mem0ai/mem0
![]() 파이토치 한국 사용자 모임
파이토치 한국 사용자 모임![]() 이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일
이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일![]() 로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
![]() 아래
아래![]() 쪽에 좋아요
쪽에 좋아요![]() 를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~
를 눌러주시면 뉴스 발행에 힘이 됩니다~ ![]()
이 글은 GPT 모델로 정리한 글을 바탕으로 한 것으로, 원문의 내용 또는 의도와 다르게 정리된 내용이 있을 수 있습니다. 관심있는 내용이시라면 원문도 함께 참고해주세요! 읽으시면서 어색하거나 잘못된 내용을 발견하시면 덧글로 알려주시기를 부탁드립니다. ![]()
파이토치 한국 사용자 모임
![]() 이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일
이 정리한 이 글이 유용하셨나요? 회원으로 가입하시면 주요 글들을 이메일![]() 로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
로 보내드립니다! (기본은 Weekly지만 Daily로 변경도 가능합니다.)
![]() 아래
아래![]() 쪽에 좋아요
쪽에 좋아요![]() 를 눌러주시면 새로운 소식들을 정리하고 공유하는데 힘이 됩니다~
를 눌러주시면 새로운 소식들을 정리하고 공유하는데 힘이 됩니다~ ![]()